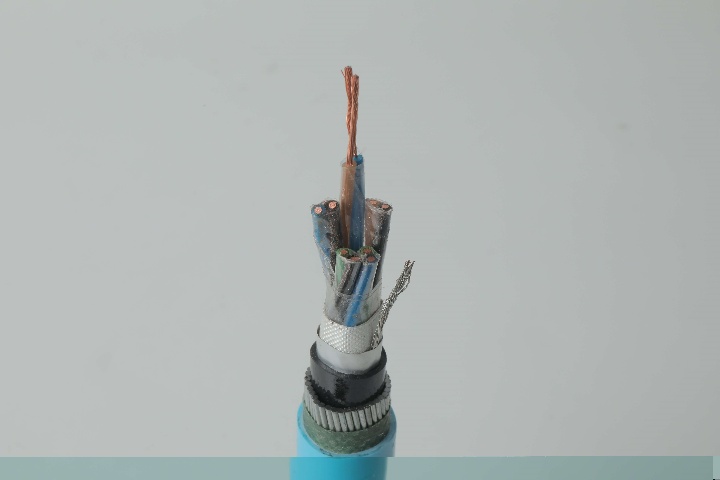
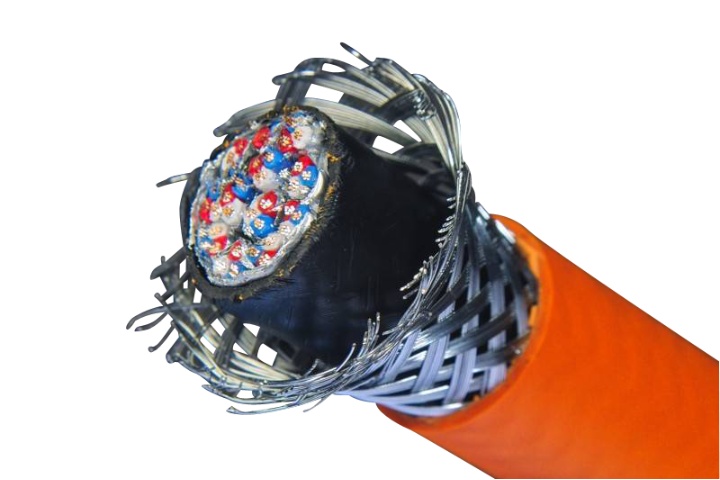
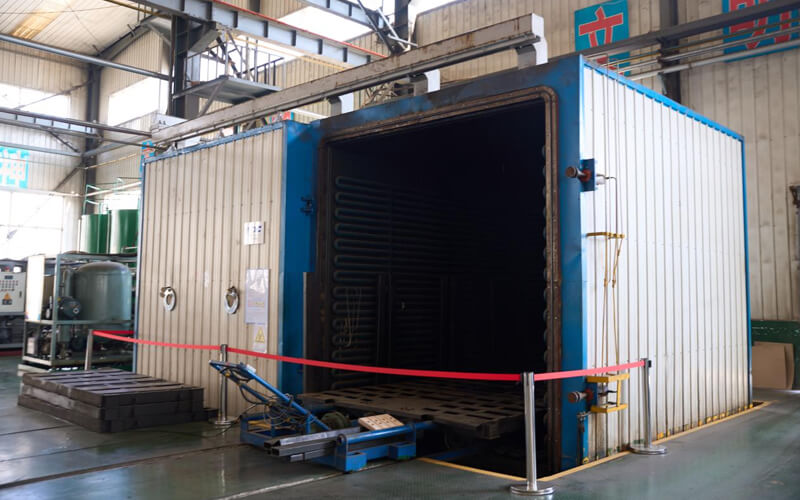
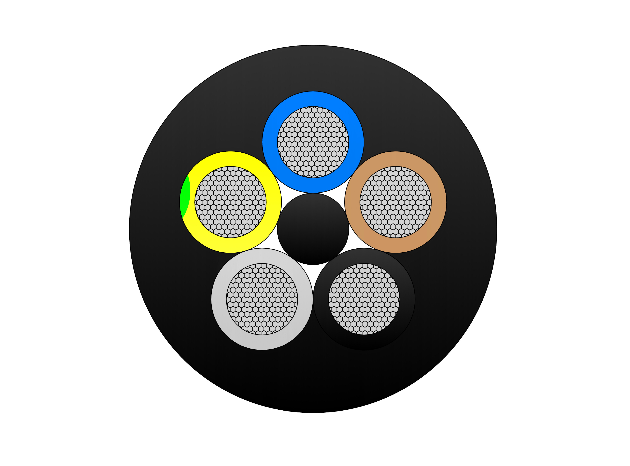
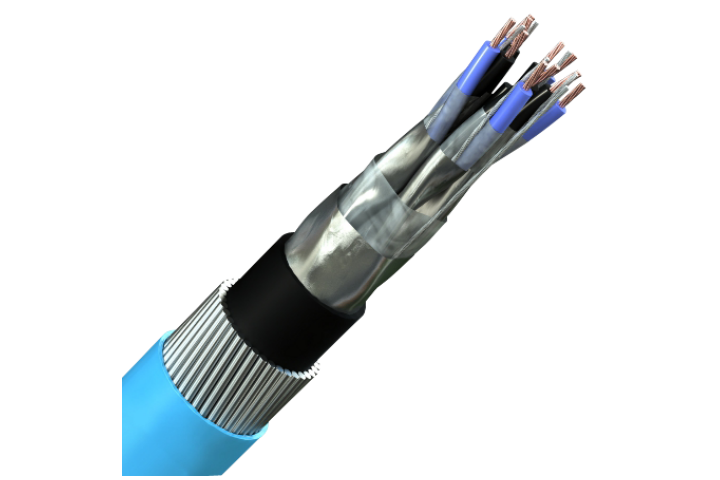
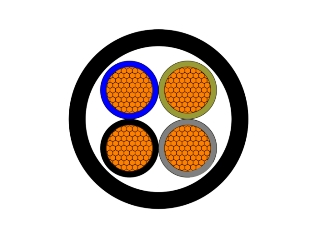
Instrumentation Cables—XLPE Insulated, Overall Screened, DRYLAM Layered, Wire Armoured PVC Sheathed Cables(CU/XLPE/OSCR/DRYLAM/SWA/PVC)
- Standard BS EN 50288-7, IEC 60502-1 (General)
Construction
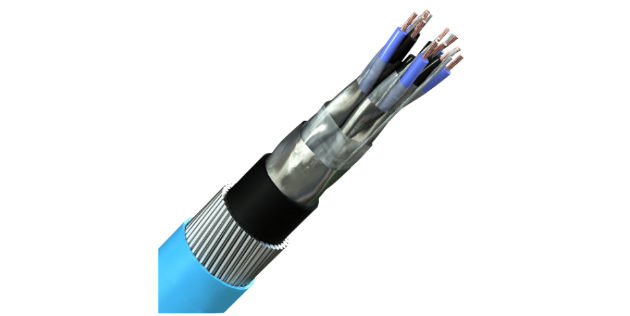
Conductor
Insulation
Individual and Overall Screen
Armour
Inner and Outer Sheath
Technical Specifications
| Conductor Size | Max. Conductor DC Resistance at 20°C for Plain Copper |
Max. Conductor DC Resistance at 20°C for Tinned Copper |
||
| Solid, Class - 1 & Stranded, Class - 2 |
Flexible, Class-5 | Solid, Class - 1 & Stranded, Class - 2 |
Flexible, Class-5 | |
| [mm2] | [Ω/km] | [Ω/km] | [Ω/km] | [Ω/km] |
| 0.50 | 36.72 | 39.78 | 37.434 | 40.902 |
| 0.75 | 24.99 | 26.52 | 25.296 | 27.234 |
| 1.00 | 18.462 | 19.89 | 18.564 | 20.4 |
| 1.50 | 12.342 | 13.566 | 12.444 | 13.974 |
| 2.50 | 7.5582 | 8.1396 | 7.7112 | 8.3742 |
| Conductor Size | Insulation Thickness | |||
| 90V | 300V | 500V | 1000V | |
| [mm2] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] |
| 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.70 |
| 0.75 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.70 |
| 1.00 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.70 |
| 1.50 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.70 |
| 2.50 | - | - | 0.53 | 0.70 |
| Conductor Size | Mutual Capacitance | Max. Continuous Operating Temperature | Inductance to Resistance Ratio (L/R) |
||
| XLPE | PVC | XLPE or HR - PVC | PVC | ||
| [mm2] | [nF/km] | [nF/km] | [°C] | [°C] | [μH/Ω] |
| 0.50 | 150 | 250 | 90 | 70 | < 25 |
| 0.75 | 150 | 250 | 90 | 70 | < 25 |
| 1.00 | 150 | 250 | 90 | 70 | < 25 |
| 1.50 | 150 | 250 | 90 | 70 | < 40 |
| 2.50 | 150 | 250 | 90 | 70 | < 60 |
| Number of Pair | Cable OD | Cable Weight | Drum Length | ||||||||
| 0.5mm² | 0.75mm² | 1.0mm² | 1.5mm² | 2.5mm² | 0.5mm² | 0.75mm² | 1.0mm² | 1.5mm² | 2.5mm² | ||
| [Nos] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [m] |
| 1 | 16.5 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 19.0 | 440 | 460 | 475 | 505 | 575 | 1000 |
| 2 | 19.0 | 20.0 | 20.5 | 21.5 | 24.0 | 555 | 590 | 620 | 670 | 805 | 1000 |
| 5 | 21.5 | 23.0 | 23.5 | 25.0 | 28.5 | 680 | 760 | 815 | 905 | 1275 | 1000 |
| 10 | 26.5 | 28.5 | 29.5 | 32.0 | 36.5 | 940 | 1200 | 1310 | 1505 | 1920 | 1000 |
| 20 | 32.0 | 34.0 | 35.5 | 38.5 | 45.0 | 1445 | 1655 | 1840 | 2155 | 3105 | 1000 |
| 30 | 36.0 | 38 | 40.5 | 44.5 | 1775 | 2055 | 2330 | 3030 | 500 | ||
| Number of Triad | Cable OD | Cable Weight | Drum Length | ||||||||
| 0.5mm² | 0.75mm² | 1.0mm² | 1.5mm² | 2.5mm² | 0.5mm² | 0.75mm² | 1.0mm² | 1.5mm² | 2.5mm² | ||
| [Nos] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [m] |
| 1 | 16.5 | 17.0 | 17.5 | 18.5 | 19.5 | 455 | 480 | 500 | 545 | 620 | 1000 |
| 2 | 20.0 | 21.0 | 21.5 | 23.0 | 25.5 | 595 | 645 | 685 | 770 | 920 | 1000 |
| 5 | 23.0 | 24.0 | 25.0 | 27.0 | 31.0 | 780 | 855 | 930 | 1075 | 1520 | 1000 |
| 10 | 29.0 | 31.0 | 32.5 | 34.5 | 40.5 | 1235 | 1410 | 1555 | 1795 | 2585 | 1000 |
| 20 | 34.5 | 37.0 | 39.0 | 43.0 | 1705 | 1990 | 2240 | 2910 | 500 | ||
| 30 | 39.0 | 42.5 | 45.0 | 2125 | 2760 | 3155 | 500 | ||||
| Number of Quad | Cable OD | Cable Weight | Drum Length | ||||||||
| 0.5mm² | 0.75mm² | 1.0mm² | 1.5mm² | 2.5mm² | 0.5mm² | 0.75mm² | 1.0mm² | 1.5mm² | 2.5mm² | ||
| [Nos] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [kg/km] | [m] |
| 1 | 17.0 | 17.5 | 18.5 | 19.0 | 20.5 | 480 | 510 | 540 | 585 | 680 | 1000 |
| 2 | 22.5 | 23.5 | 24.5 | 26.0 | 30.0 | 700 | 770 | 825 | 925 | 1295 | 1000 |
| 5 | 26.0 | 28.5 | 29.5 | 32.0 | 36.5 | 930 | 1195 | 1305 | 1500 | 1915 | 1000 |
| 10 | 34.0 | 36.5 | 38.0 | 42.0 | 48.5 | 1540 | 1760 | 1950 | 2530 | 3300 | 1000 |
| 20 | 42.0 | 45.0 | 47.5 | 2410 | 2805 | 3160 | 500 | ||||
| 30 | 47.5 | 3010 | 500 | ||||||||
Note: Cable OD and Cable weight are subject to change based on the latest manufacturing practice.
Quality Control

Raw Material Test
Raw Material Test is the initial quality control stage for CU/XLPE/OSCR/DRYLAM/SWA/PVC instrumentation cables. Copper conductors are tested for electrical conductivity, tensile strength, and dimensional consistency. XLPE insulation compounds undergo thermal aging, elongation, and insulation resistance testing. Screening materials are inspected for conductivity and shielding effectiveness. DRYLAM water-blocking tapes and yarns are evaluated for swelling performance and moisture absorption capacity. Steel wire armour is tested for mechanical strength and flexibility, while PVC sheath materials are examined for flame retardancy and environmental resistance. Only materials that meet all technical specifications are approved for production.

Process inspection
Process Inspection ensures stable manufacturing quality of CU/XLPE/OSCR/DRYLAM/SWA/PVC instrumentation cables. XLPE insulation extrusion is monitored for thickness uniformity and concentricity. The overall screening process is inspected to confirm complete coverage and electrical continuity. DRYLAM layering is checked to ensure correct placement and effective water-blocking performance. Armouring is inspected for correct wire tension and lay length. PVC sheathing is controlled for surface quality and dimensional accuracy. Continuous in-process inspections ensure compliance with design and performance requirements.

Finished Product
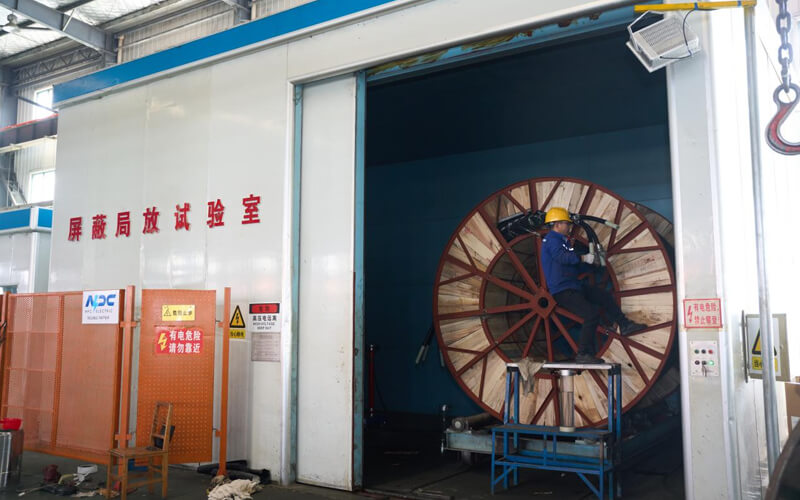
Finished Product Test verifies the final performance of CU/XLPE/OSCR/DRYLAM/SWA/PVC instrumentation cables. Electrical tests include conductor resistance, insulation resistance, and voltage withstand testing. Mechanical tests assess tensile strength, bending capability, and impact resistance. Water penetration tests confirm the effectiveness of the DRYLAM layer. Final visual and dimensional inspections ensure correct construction, marking, and overall workmanship before shipment.
Application
Technical Advantages
Product Packaging
Related Products
FAQ From Customers
-
What are the advantages of power cables and overhead lines?(1) Reliable operation, because it is installed in a hidden place such as underground, it is less damaged by external forces, has less chance of failure, and the power supply is safe, and it will not cause harm to people; (2) The maintenance workload is small and frequent inspections are not required; (3) No need to erect towers; (4) Help improve power factor.
-
Which aspects should be considered when choosing the cross section of a power cable?(1) The long-term allowable working current of the cable; (2) Thermal stability once short circuited; (3) The voltage drop on the line cannot exceed the allowable working range.
-
What are the measures for cable fire prevention?(1) Use flame-retardant cables; (2) Use fireproof cable tray; (3) Use fireproof paint; (4) Fire partition walls and fire baffles are installed at cable tunnels, mezzanine exits, etc.; (5) Overhead cables should avoid oil pipelines and explosion-proof doors, otherwise local pipes or heat insulation and fire prevention measures should be taken.
-
What should be paid attention to during the transportation and handling of cables?(1) During transportation, loading and unloading, cables and cable reels should not be damaged. It is strictly forbidden to push the cable reels directly from the vehicle. Generally, cables should not be transported and stored flat. (2) Before transporting or rolling the cable reel, ensure that the cable reel is firm, the cable is wound tightly, the oil pipe between the oil-filled cable and the pressure oil tank should be fixed without damage, the pressure oil tank should be firm, and the pressure indication should meet the requirements.
-
What inspections should be carried out for the acceptance of cable lines?(1) The cable specifications should meet the regulations, the arrangement should be neat, no damage, and the signs should be complete, correct and clear; (2) The fixed bending radius of the cable, the related distance and the wiring of the metal sheath of the single-core power cable should meet the requirements; (3) The cable terminal and the middle head should not leak oil, and the installation should be firm. The oil pressure of the oil-filled cable and the meter setting should meet the requirements; (4) Good grounding; (5) The color of the cable terminal is correct, and the metal parts such as the bracket are completely painted; (6) There should be no debris in the cable trench, tunnel, and bridge, and the cover should be complete.