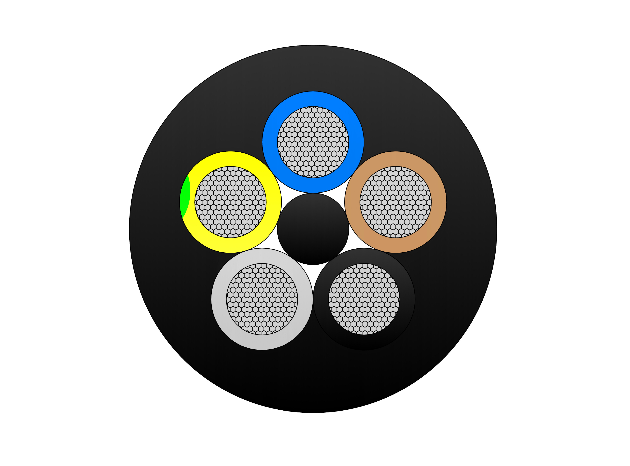
N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable(6/10kV, 8.7/15KV,12/20kV, 18/30kV)
-
Voltage Rating(Uo/U)(Um)
6/10 (12) KV
8.7/15 (17.5)KV
12/20 (24)KV
18/30 (36)KV -
Test Voltage
21kV AC 50Hz (5 mins)
42kV AC 50Hz (5 mins)
63kV AC 50Hz (5 mins) - Maxi conductor operating temp 90°C
- Initial temp at S.C.C 80°C
- Maxi conductor temp during S.C 250°C
- Minimum Bending Radius 15 x overall diameter
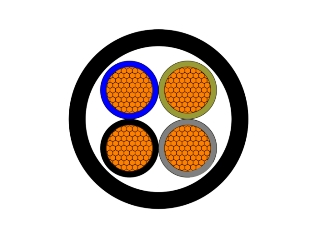
Construction
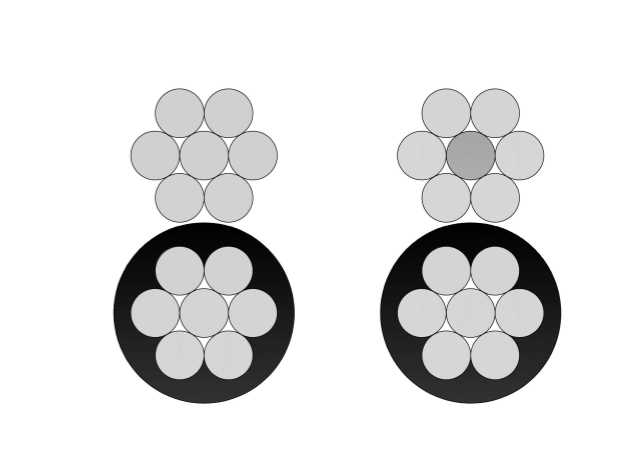
Conductor
Insulation
Inner Layer
Outer Layer
Screen
Outer Sheath
Sheath Color
Manufacturer Standard
Flame retardant
Technical Specifications
| No of Cores |
Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Screen Cross Section Area |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Approximate Weight |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | |
| 3 | 50 | 16 | 3.4 | 2.4 | 43.8 | 2752 |
| 3 | 70 | 16 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 47.9 | 3513 |
| 3 | 95 | 16 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 51.1 | 4399 |
| 3 | 120 | 16 | 3.4 | 2.8 | 54.3 | 5241 |
| 3 | 150 | 25 | 3.4 | 2.9 | 58.0 | 6300 |
| 3 | 185 | 25 | 3.4 | 3.0 | 61.4 | 7440 |
| 3 | 240 | 25 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 66.8 | 9359 |
| 3 | 300 | 25 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 72.2 | 11267 |
| 3 | 400 | 35 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 78.4 | 14127 |
| 3 | 500 | 35 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 86.2 | 17513 |
| No of Cores |
Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Screen Cross Section Area |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Approximate Weight |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | |
| 3 | 50 | 16 | 4.5 | 2.6 | 48.5 | 3092 |
| 3 | 70 | 16 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 52.6 | 3882 |
| 3 | 95 | 16 | 4.5 | 2.8 | 55.6 | 4764 |
| 3 | 120 | 16 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 58.9 | 5637 |
| 3 | 150 | 25 | 4.5 | 3.1 | 62.5 | 6712 |
| 3 | 185 | 25 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 65.9 | 7877 |
| 3 | 240 | 25 | 4.5 | 3.3 | 71.3 | 9832 |
| 3 | 300 | 25 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 76.9 | 11814 |
| 3 | 400 | 35 | 4.5 | 3.7 | 82.9 | 14682 |
| 3 | 500 | 35 | 4.5 | 3.9 | 90.7 | 18123 |
| No of Cores |
Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Screen Cross Section Area |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Approximate Weight |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | |
| 3 | 50 | 16 | 5.5 | 2.8 | 53.3 | 3474 |
| 3 | 70 | 16 | 5.5 | 2.9 | 57.3 | 4288 |
| 3 | 95 | 16 | 5.5 | 3.0 | 59.9 | 5173 |
| 3 | 120 | 16 | 5.5 | 3.1 | 62.9 | 6028 |
| 3 | 150 | 25 | 5.5 | 3.2 | 67.0 | 7155 |
| 3 | 185 | 25 | 5.5 | 3.3 | 70.5 | 8352 |
| 3 | 240 | 25 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 76.1 | 10383 |
| 3 | 300 | 25 | 5.5 | 3.6 | 81.4 | 12356 |
| 3 | 400 | 35 | 5.5 | 3.9 | 87.7 | 15322 |
| 3 | 500 | 35 | 5.5 | 4.1 | 95.2 | 18760 |
| No of Cores |
Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Screen Cross Section Area |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Approximate Weight |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | |
| 3 | 50 | 16 | 8 | 3.1 | 64.5 | 4471 |
| 3 | 70 | 16 | 8 | 3.2 | 68.1 | 5332 |
| 3 | 95 | 16 | 8 | 3.4 | 71.3 | 6324 |
| 3 | 120 | 16 | 8 | 3.5 | 74.5 | 7265 |
| 3 | 150 | 25 | 8 | 3.6 | 78.6 | 8463 |
| 3 | 185 | 25 | 8 | 3.7 | 82.1 | 9720 |
| 3 | 240 | 25 | 8 | 3.9 | 87.7 | 11853 |
| 3 | 300 | 25 | 8 | 4.0 | 93 | 13919 |
| 3 | 400 | 35 | 8 | 4.3 | 99.1 | 16960 |
| 3 | 500 | 35 | 8 | 4.5 | 106.8 | 20577 |
Quality Control

Raw Material Test
For the N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable (6/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 18/30kV), raw material testing commences with copper certification for conductivity and ductility. XLPE granules are tested for crosslinking agent, thermal stability, and contamination via hot set pre-checks and TGA. Individual screen materials undergo thickness uniformity and bonding verification. PVC compound faces Congo red testing, volume resistivity, and migration analysis. Fillers and water-blocking elements are checked for expansion and compatibility. The structured process: receipt inspection, random sampling, physical/mechanical testing (yield, elongation), chemical spectroscopy confirmation, accelerated aging/UV trials, and material release decision. This rigorous evaluation secures premium inputs, establishing the base for the N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable's dielectric excellence, per-core screening reliability.

Process inspection
Process inspection during N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable (6/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 18/30kV) manufacturing involves real-time quality assurance. Conductor stranding monitors surface defects and compactness. Triple co-extrusion ensures void-free shields and insulation with capacitance gauges. Per-core screening controls application density and tape integrity. Assembly verifies core twisting, filling symmetry, and bedding. PVC sheath extrusion includes online spark testing and ovality control. Critical steps: pre-extrusion dryness verification, parameter stabilization, real-time eccentricity monitoring, gel fraction sampling, partial discharge intermediate checks, and defect removal protocols. This multi-stage control maintains the N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable's precise three-core geometry, reliable individual screening, strong sheath adhesion, and IEC 60502-2 compliance.

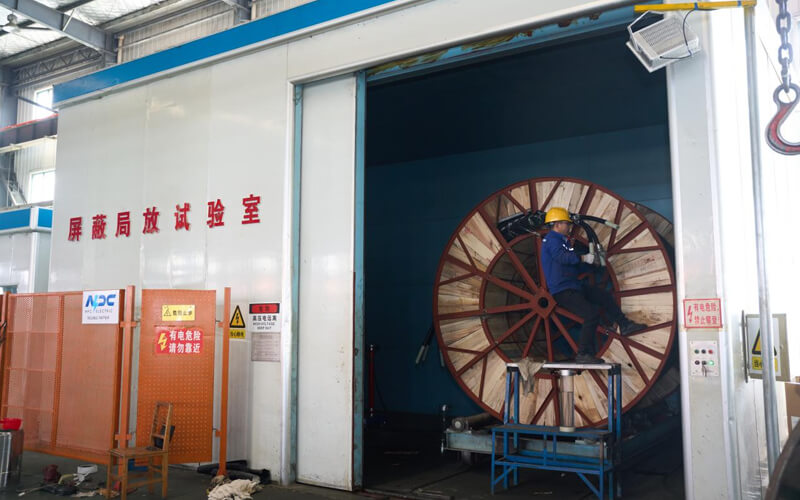
Finished Product
Completed N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable (6/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 18/30kV) reels face strict factory tests. Mandatory routines: DC resistance, per-core screen resistance, high-potential AC test, partial discharge (≤5pC), and thickness checks. Extended tests include lightning impulse, long-duration voltage, heat cycling, and water tightness. Tan delta and capacitance measurements follow. The sequential process: sample conditioning, voltage ramp application, PD monitoring, timed exposure to heat/water, recovery phase inspection, property re-measurement, and documentation. Additional verifications cover phase balance and marking permanence. Passing all confirms the N2XSEY Medium Voltage Power Cable's electrical uniformity, screening effectiveness, three-core reliability, and suitability for critical medium voltage underground installations.
Application
Technical Advantages
Product Packaging
Related Products
FAQ From Customers
-
What are the advantages of power cables and overhead lines?(1) Reliable operation, because it is installed in a hidden place such as underground, it is less damaged by external forces, has less chance of failure, and the power supply is safe, and it will not cause harm to people; (2) The maintenance workload is small and frequent inspections are not required; (3) No need to erect towers; (4) Help improve power factor.
-
Which aspects should be considered when choosing the cross section of a power cable?(1) The long-term allowable working current of the cable; (2) Thermal stability once short circuited; (3) The voltage drop on the line cannot exceed the allowable working range.
-
What are the measures for cable fire prevention?(1) Use flame-retardant cables; (2) Use fireproof cable tray; (3) Use fireproof paint; (4) Fire partition walls and fire baffles are installed at cable tunnels, mezzanine exits, etc.; (5) Overhead cables should avoid oil pipelines and explosion-proof doors, otherwise local pipes or heat insulation and fire prevention measures should be taken.
-
What should be paid attention to during the transportation and handling of cables?(1) During transportation, loading and unloading, cables and cable reels should not be damaged. It is strictly forbidden to push the cable reels directly from the vehicle. Generally, cables should not be transported and stored flat. (2) Before transporting or rolling the cable reel, ensure that the cable reel is firm, the cable is wound tightly, the oil pipe between the oil-filled cable and the pressure oil tank should be fixed without damage, the pressure oil tank should be firm, and the pressure indication should meet the requirements.
-
What inspections should be carried out for the acceptance of cable lines?(1) The cable specifications should meet the regulations, the arrangement should be neat, no damage, and the signs should be complete, correct and clear; (2) The fixed bending radius of the cable, the related distance and the wiring of the metal sheath of the single-core power cable should meet the requirements; (3) The cable terminal and the middle head should not leak oil, and the installation should be firm. The oil pressure of the oil-filled cable and the meter setting should meet the requirements; (4) Good grounding; (5) The color of the cable terminal is correct, and the metal parts such as the bracket are completely painted; (6) There should be no debris in the cable trench, tunnel, and bridge, and the cover should be complete.