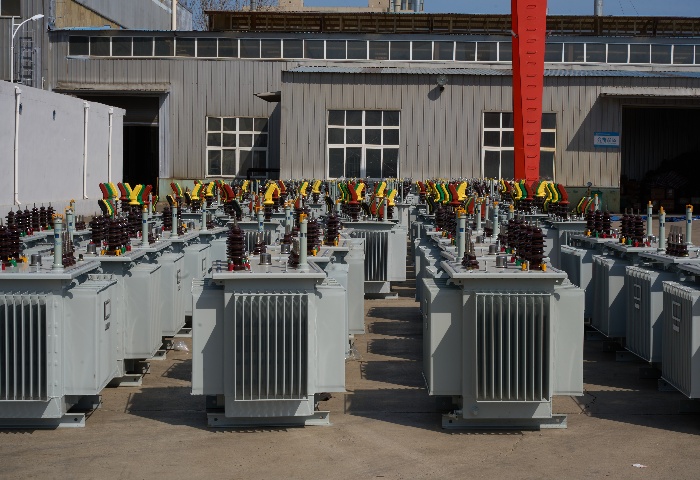
What Does a Power Pole Transformer Do?
Electricity is generated at power plants at very high voltages—often in the range of thousands of volts—to allow it to travel long distances through power lines with minimal loss. However, this high-voltage electricity isn't suitable for use in homes and small businesses. Appliances and residential systems typically operate at much lower voltages, such as 120 or 220 volts.
This is where distribution transformers come in, especially electric pole transformers, which step down the high voltage from transmission lines to safe, usable levels.
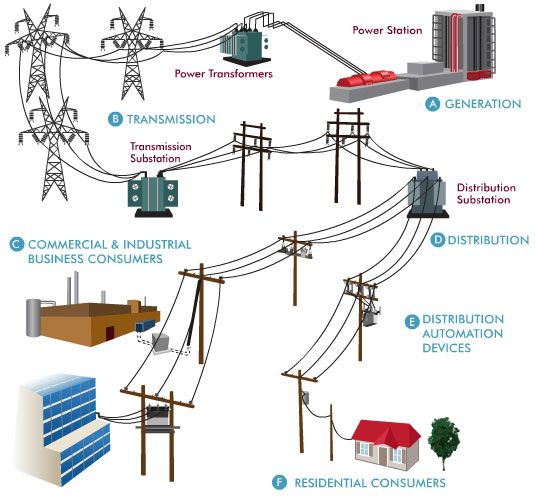
2. What Is a Power Pole Transformer?
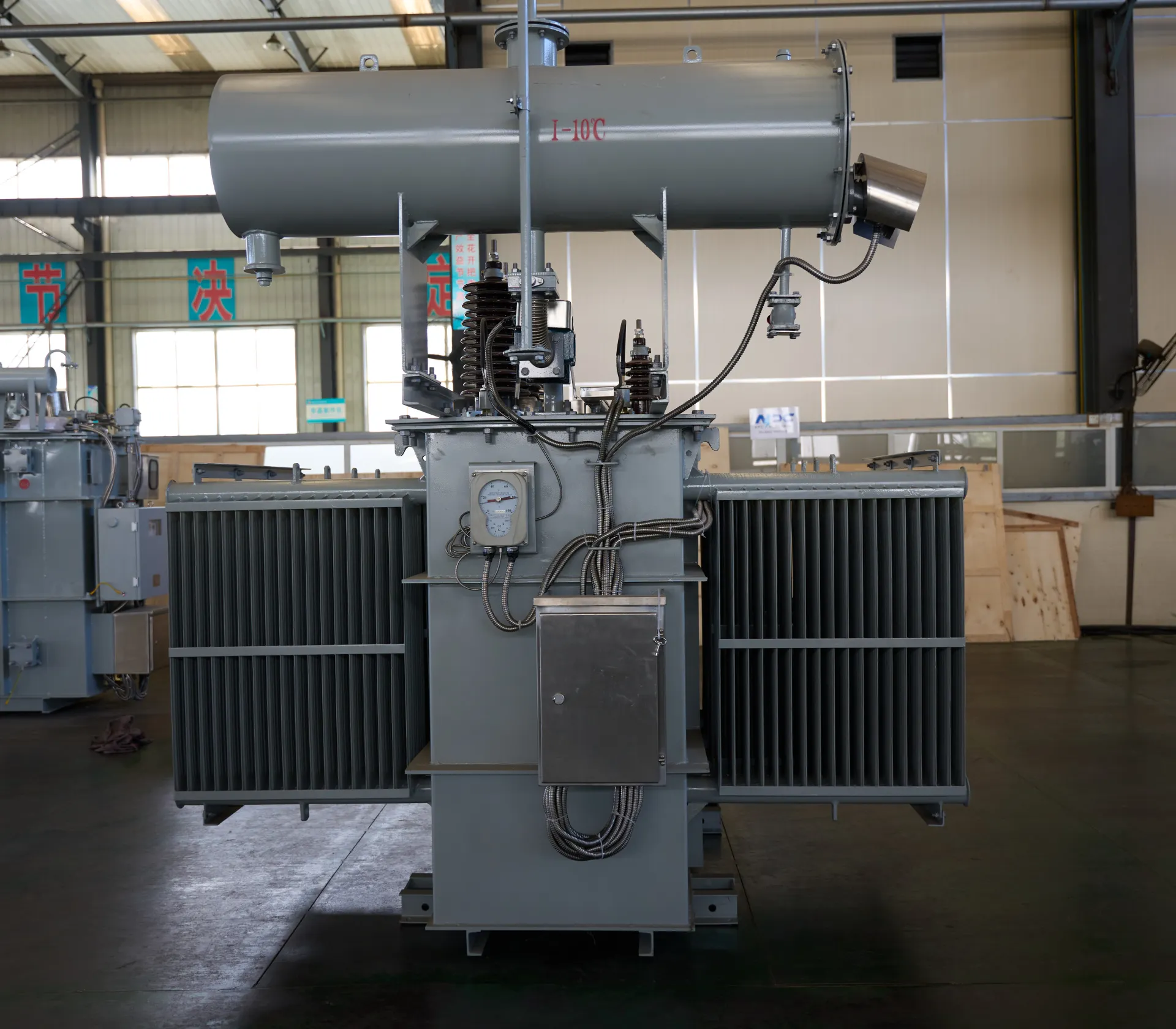
A power pole transformer, also known as a pole mounted transformer, is a type of distribution transformer that is installed on utility poles. These transformers are designed to reduce the high voltage carried by distribution networks down to a level that is suitable for household or commercial use.
There are several types of pole transformers, but the most common in residential areas is the single phase pole mounted transformer.
3. How Does a Pole Mounted Transformer Work?
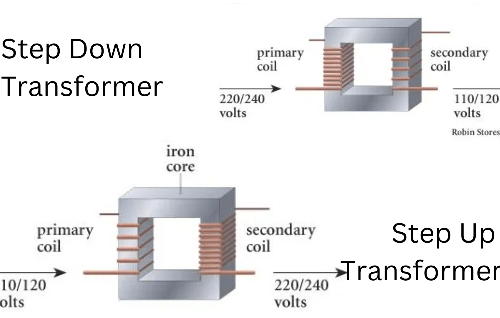
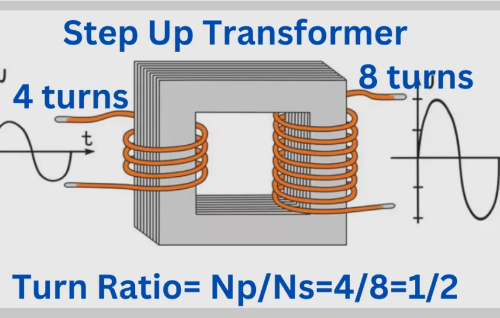
A pole mounted transformer operates using electromagnetic induction. Inside the transformer, there are two sets of windings—primary and secondary—wrapped around a magnetic core.
- Primary winding connects to the high-voltage distribution network
- Secondary winding connects to lower-voltage service lines that lead into buildings
The transformer reduces the voltage using the ratio of turns in the coils, stepping down the voltage to a usable level, usually 120V or 240V, for everyday electrical devices.
4. Single Phase Transformers: Common in Residential Areas
The single phase transformer is widely used in suburban and rural settings where the power demands are relatively low. A single phase pole mounted transformer typically serves a few houses or a small building.
Advantages include:
- Simple construction and installation
- Cost-effective
- Easy maintenance
In larger urban areas or commercial zones, three-phase systems or pad mounted transformers (installed at ground level) might be more appropriate.
5. Components of an Electric Pole Transformer
A typical electric pole transformer includes:
- Tank: Holds insulating oil and the transformer core
- Bushings: For connecting high-voltage and low-voltage lines
- Lightning Arresters: Protect from voltage spikes
- Fuse Cutout: Acts as a circuit breaker
- Ground Wire: Ensures safety
6. Importance in the Electric Power Distribution System
The electric power distribution system relies heavily on pole mounted transformers to ensure that electricity is delivered safely and efficiently to consumers.
Without them:
- Power would be too high for direct use
- Electrical appliances could be damaged
- User safety would be at risk
Because they're installed at strategic points throughout the distribution network, these transformers help maintain voltage regulation and system stability.
7. Pole Transformers vs. Pad Mounted Transformers
While both are distribution transformers, their applications differ:
|
Feature |
Pole Mounted Transformer |
Pad Mounted Transformer |
|
Location |
Mounted on utility poles |
Installed at ground level |
|
Use case |
Rural/suburban, low power demand |
Urban/commercial, higher power loads |
|
Phase |
Often single phase |
Commonly three-phase |
|
Maintenance |
Easier to access |
Requires safety barriers |
Each has its place depending on population density, power requirements, and infrastructure layout.
8. Typical Ratings and Capacities
A common specification you might see is a 25 kVA power pole transformer. The “kVA” stands for kilovolt-amperes, a unit of apparent power.
Common sizes include:
- 10 kVA: Suitable for 1–2 homes
- 25–50 kVA: Typical for small buildings or multiple homes
- 75 kVA and above: For commercial or small industrial applications
The right size depends on the expected load and number of end users.
9. Safety and Maintenance Considerations
Even though pole transformers are built for long-term reliability, regular inspection is vital. Potential risks include:
- Oil leaks
- Lightning damage
- Overloads from unexpected demand spikes
Utilities often use thermal sensors and drone inspections to monitor the condition of these transformers without needing to physically climb the pole.

10. An Essential Link in Distributing Electricity
To sum it up, a power pole transformer is a key component of the modern electrical infrastructure. It allows the safe conversion of high-voltage transmission power into usable energy for homes and businesses. Whether it's a single phase transformer serving a quiet street or a kVA power pole transformer supplying a busy community center, these devices are essential to our daily lives.
Next time you look up at a utility pole, you’ll know that the gray cylinder is doing more than just hanging there—it's distributing electricity with precision and reliability.









2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)