Differences Between Substation Transformers and Oil Immersed Transformers
1. What Is a Substation Transformer?
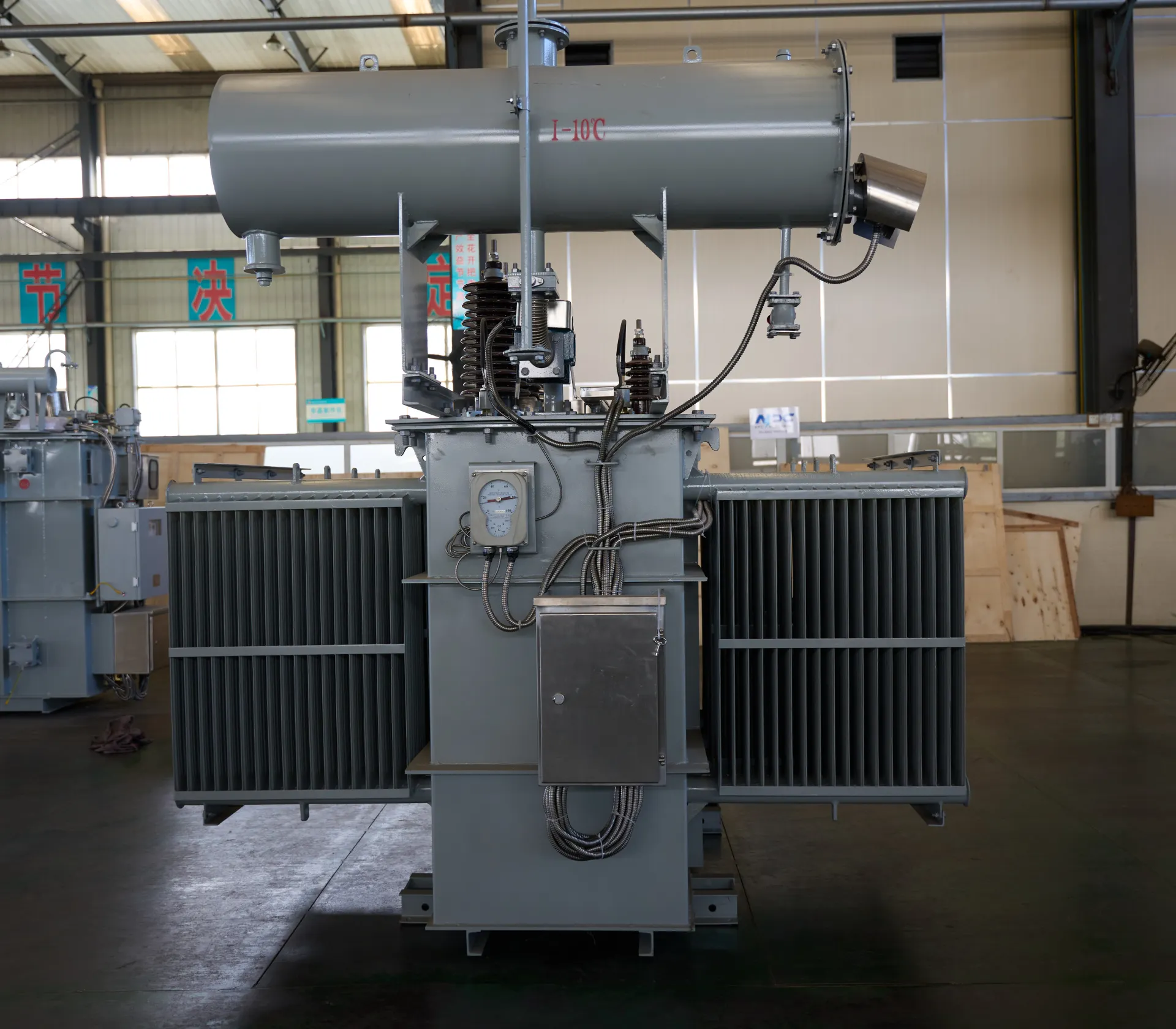
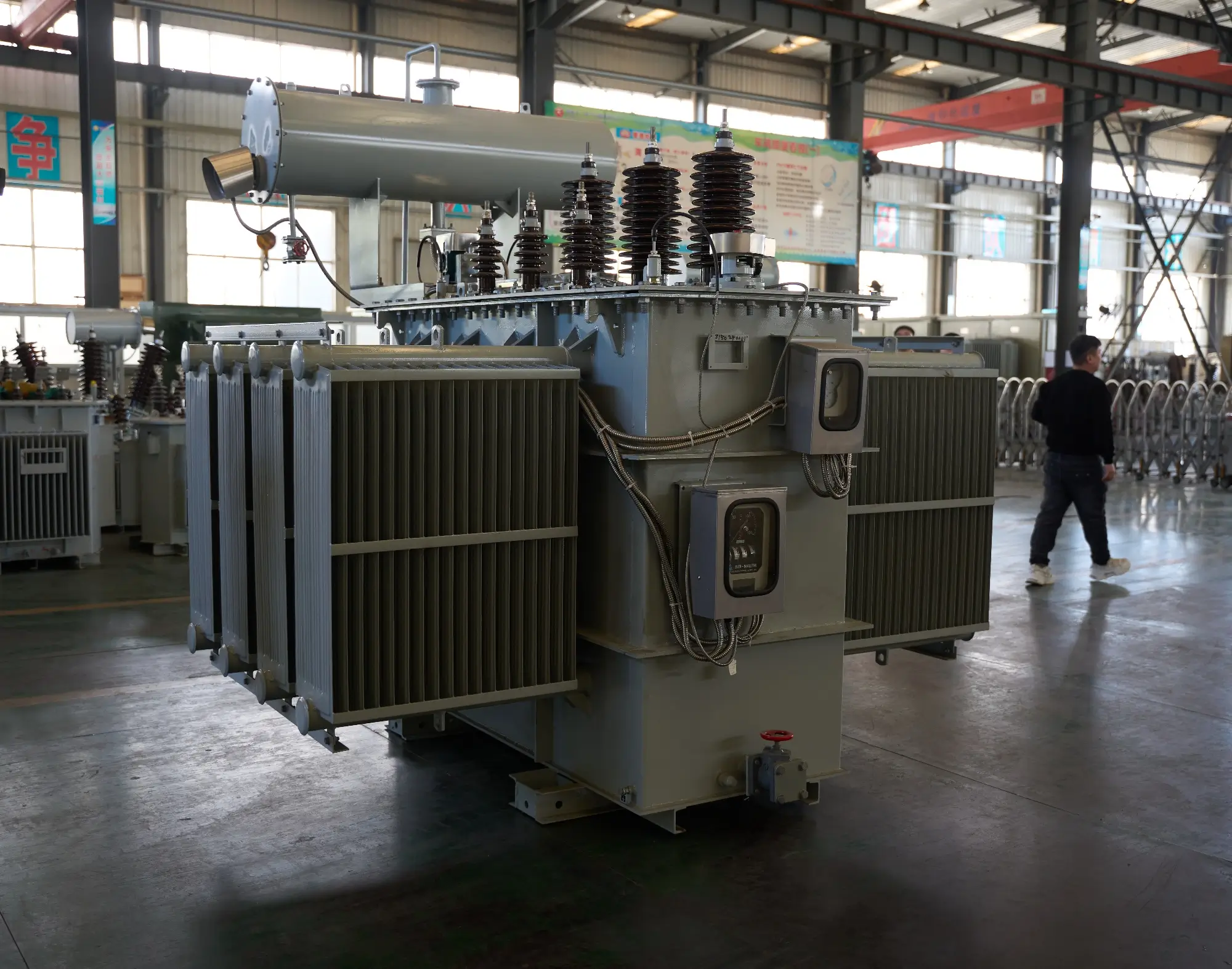
A substation transformer (often called an electrical substation transformer) is designed to step down transmission-level voltages into levels suitable for local distribution. It is the critical link in every transformer and substation system.
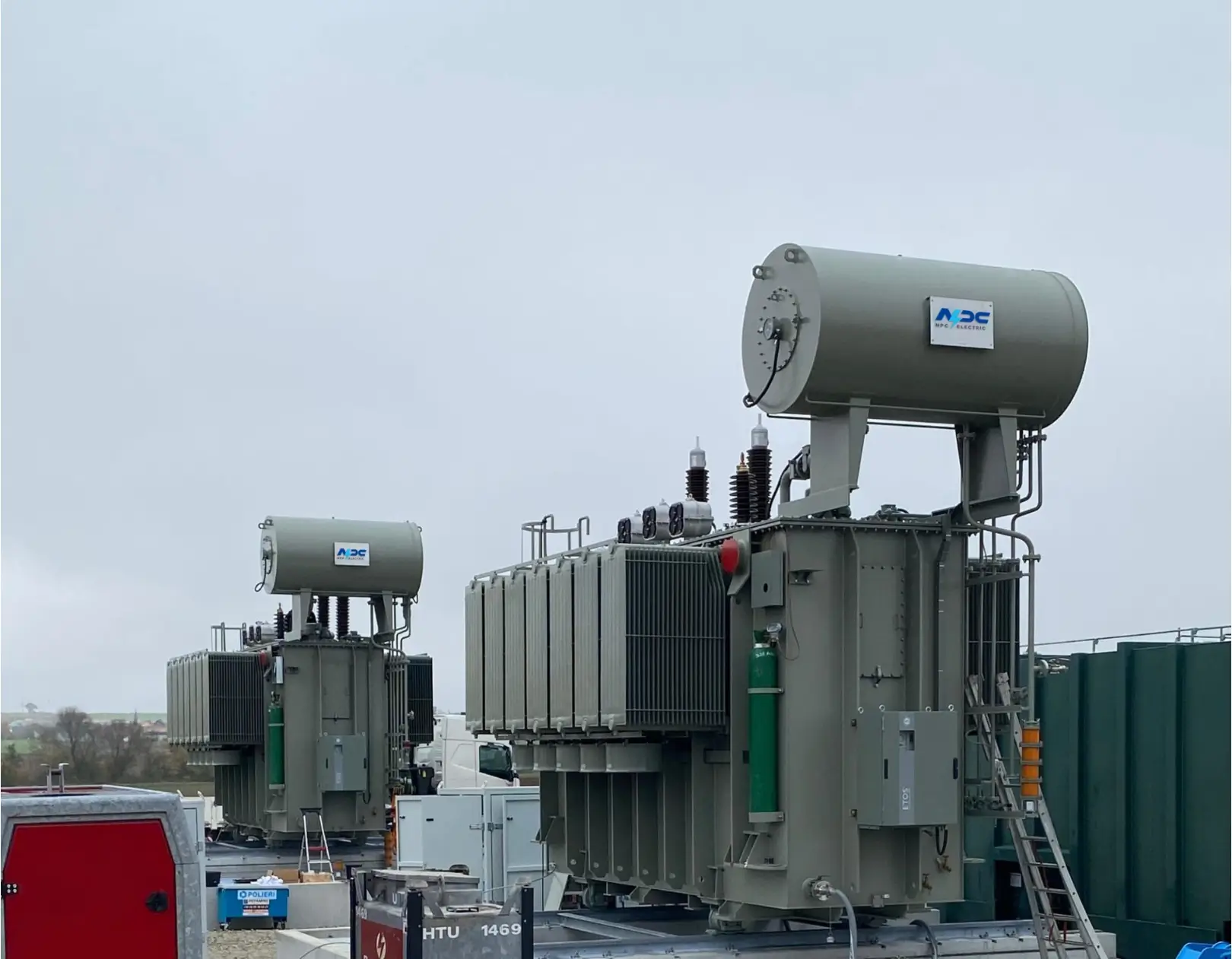
2. What Is an Oil Immersed Transformer?
An oil immersed transformer is a distribution transformer type that uses insulating oil for cooling and electrical insulation. In our factory, we build a wide range of oil immersed distribution transformers, which form the backbone of many distribution networks.
3. Key Design Differences Between Substation Transformers and Oil Immersed Transformers
- Capacity and Voltage Handling: Substation transformers handle higher voltages, while oil immersed transformers are built for medium and low voltage.
- Cooling Systems: Substation units use advanced cooling; transformers and oil immersed rely on oil circulation (ONAN, OFAF).
- Insulation and Safety: Substation designs include protective systems; oil immersed transformers depend on oil for both insulation and cooling.
4. Applications in the Distribution Network
- Substation Transformers: Installed in transformers and substation facilities to bridge transmission and distribution.
- Oil Immersed Transformers: Installed closer to consumers, serving residential, commercial, and light industrial loads.
5. Quality Control and Testing of Transformers
From my role in production, I see clear differences in testing:
- Substation Transformer Testing: impulse, short-circuit, advanced dielectric performance.
- Oil Immersed Transformer Testing: temperature rise, oil quality checks, efficiency testing.
Every transformer meets global standards before delivery.
6. Comparing Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of Substation Transformers
- High capacity
- Robust design
- Essential for high-voltage interface
Advantages of Oil Immersed Transformers
- Effective cooling system
- Cost-efficient
- Long service life with proper oil maintenance
Limitations
- Substation transformers: larger footprint, high installation cost
- Oil immersed transformers: risk of oil leakage, fire hazard compared with dry type transformers
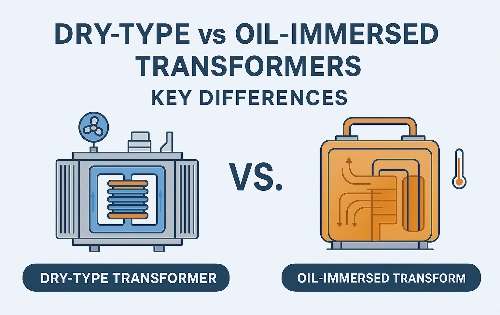
7. Oil Immersed Transformers vs Dry Type Transformers
While dry type transformers use air or resin for insulation (ideal for indoor and urban use), transformers and oil immersed remain the most efficient and reliable for outdoor distribution.
8. Choosing the Right Types of Transformers for the Distribution Network
When selecting between types of transformers, engineers must consider:
- Load requirements
- Voltage levels
- Cooling system suitability
- Safety and maintenance conditions
Conclusion: Why the Differences Matter
The difference between a substation transformer and an oil immersed transformer is not just technical—it impacts efficiency, safety, and reliability across the distribution network.
As a production-line engineer, I know that choosing the right transformer—whether substation, oil immersed, or dry type—is essential for building a dependable power system.

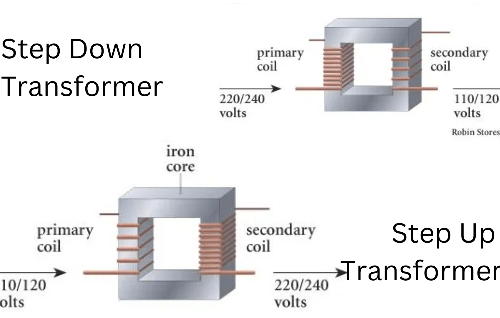
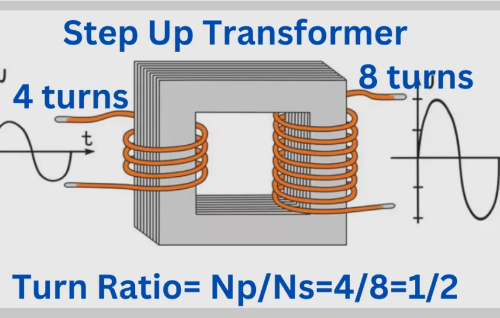





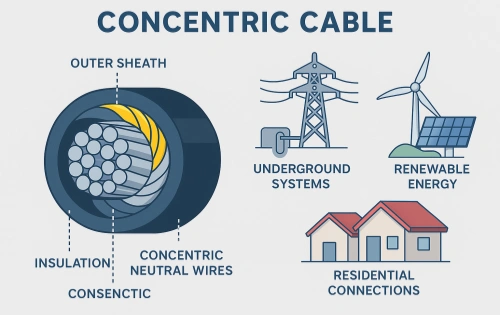



SSCHOU-mining-cable-2.webp)



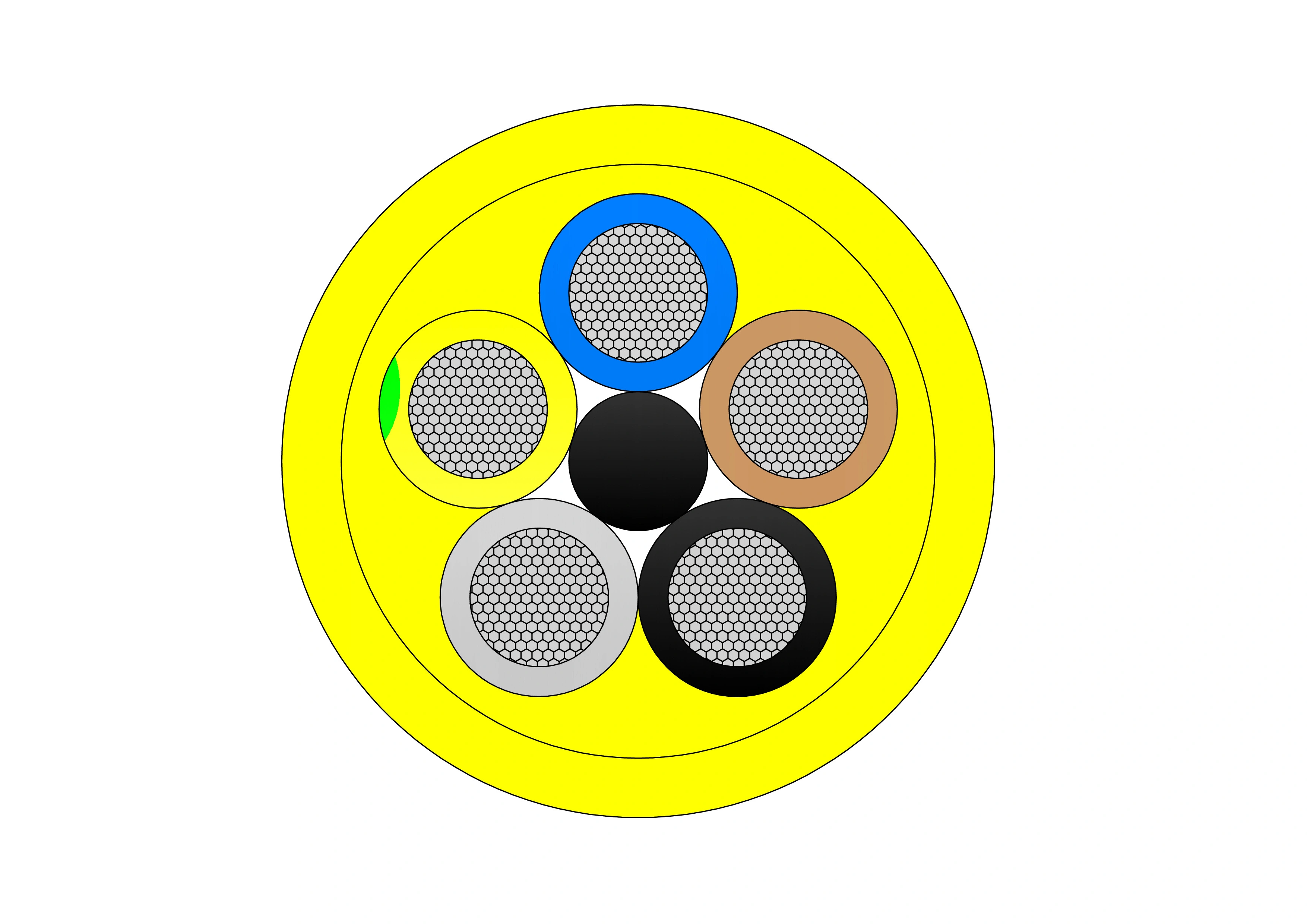
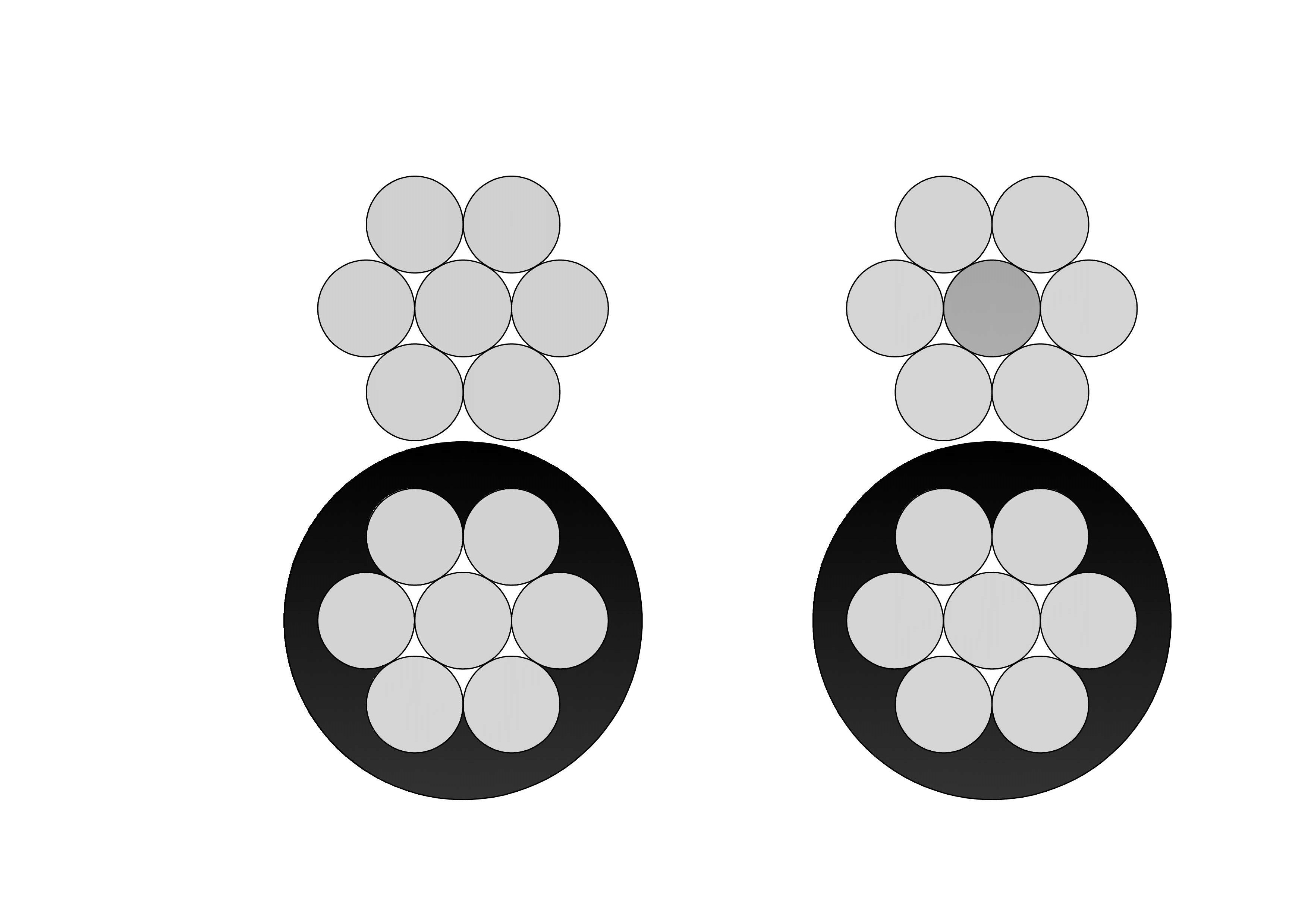


SHOUOJ-mining-cable-2.webp)