Oil Immersed Transformers Explained: How They Work and Their Role in Power Systems
Oil-immersed transformers are a critical part of electrical power systems, widely used in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. These transformers operate by using transformer oil to cool and insulate the system. The key advantage of an oil immersed transformer is its ability to manage high electrical loads while maintaining stable operation, making it essential for both industrial and residential applications.
1. What Is an Oil-Immersed Transformer?
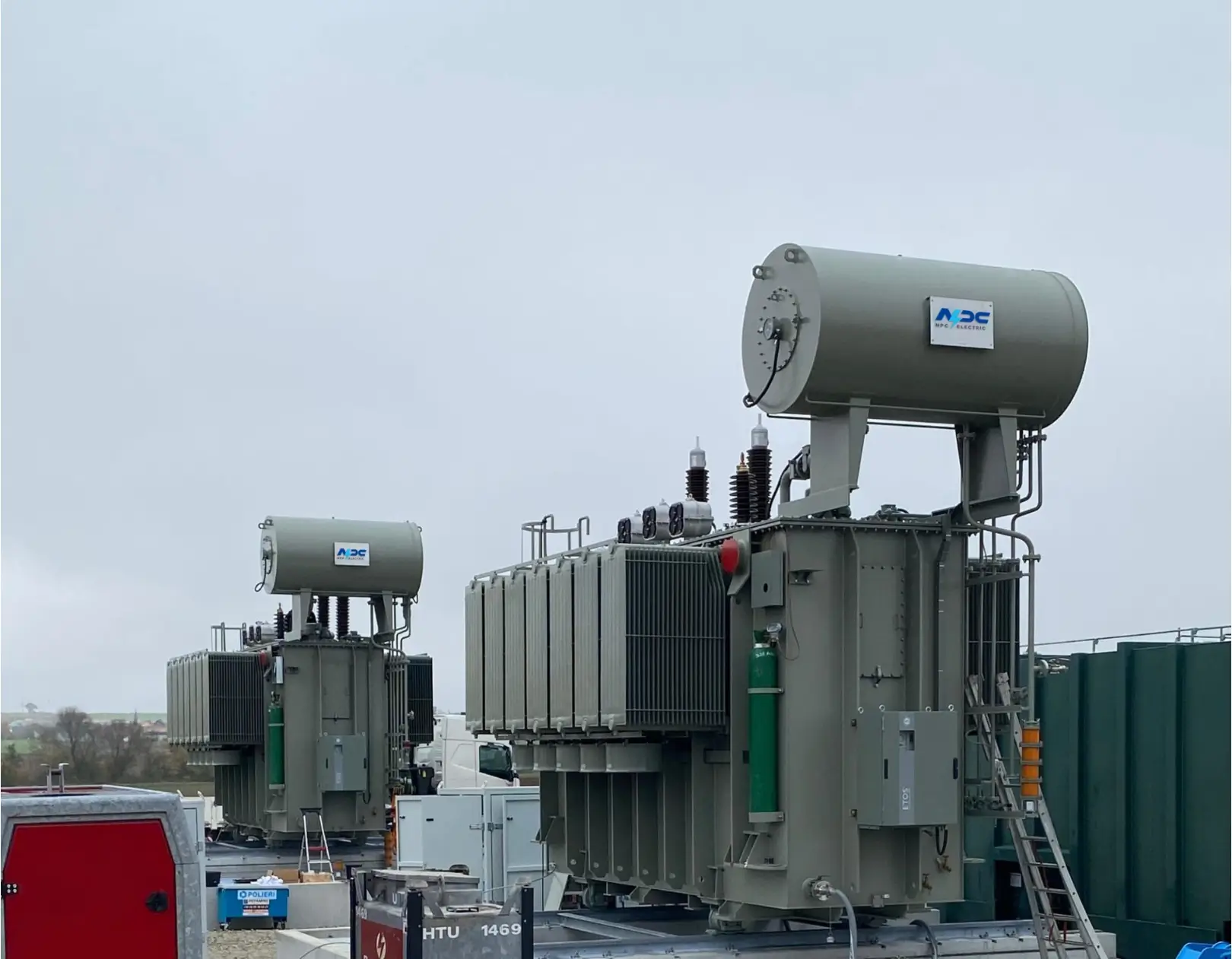
An oil-immersed transformer is a type of electrical transformer where the core and windings are submerged in oil, typically mineral oil, which serves as both an insulator and a coolant. The oil helps dissipate the heat generated by the electrical current flowing through the transformer.
These transformers are used in high-voltage applications and are typically seen in large power substations, where high electrical energy needs to be transformed into a lower voltage for safe distribution.
2. How Do Oil Immersed Transformers Work?
The basic principle behind an oil-immersed transformer is the same as any other transformer: electromagnetic induction. The primary coil (or winding) is energized by an alternating current, creating a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces a current in the secondary coil, resulting in a change in voltage.
- Step 1: The primary voltage (high voltage) is applied to the primary winding.
- Step 2: This generates a magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary winding.
- Step 3: The secondary winding provides the output voltage, which is typically lower than the primary, making it suitable for various industrial and residential applications.
However, what differentiates an oil-immersed transformer from other types is the cooling method. The transformer oil provides two main functions:
- Insulation: The oil insulates the winding from the metal parts of the transformer, preventing short circuits.
- Cooling: The oil absorbs heat generated during the energy transfer process, circulating it within the tank or radiator to dissipate the heat.
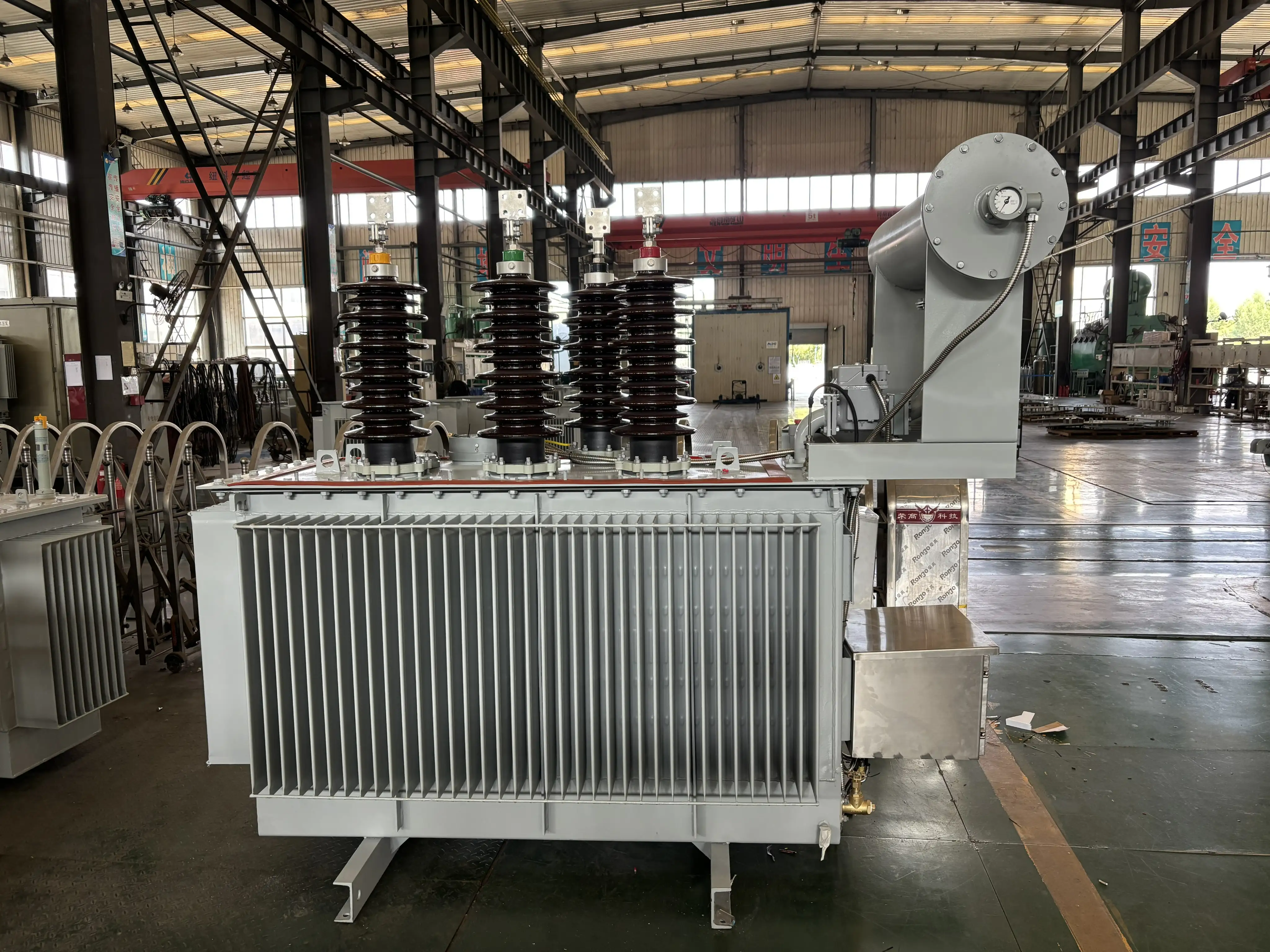
3. Design and Construction of Oil-Immersed Transformers
The design of an oil-immersed transformer typically includes the following elements:
- Core: Made of laminated silicon steel to reduce energy losses. The core creates a path for the magnetic flux.
- Windings: These are typically made of copper or aluminum and are responsible for carrying the electrical current. The primary winding is connected to the high-voltage input, and the secondary winding produces the lower output voltage.
- Tank: The entire transformer unit is housed in a steel tank filled with transformer oil. The oil not only insulates the internal components but also helps dissipate the heat generated during operation.
- Radiators: These are often attached to the tank to provide extra surface area for the cooling oil to release heat.
- Bushings: These components allow the connection of the transformer to external electrical circuits, helping to pass the electrical current safely while maintaining the oil insulation.
4. Advantages of Oil-Immersed Transformers
There are several advantages to using oil-immersed transformers:
- High Cooling Capacity: The oil cooling system allows oil-immersed transformers to handle large currents and maintain steady performance even in high-load conditions.
- Safety Features: The oil acts as an insulating medium, preventing electrical shorts, and fire-resistant oils further improve the safety of the transformer.
- Longer Lifespan: The oil provides a protective environment for the internal components, reducing wear and tear and extending the transformer’s service life.
- Efficient Heat Dissipation: Oil-immersed transformers are ideal for areas with high ambient temperatures, as the oil can handle the high heat generated by the transformer’s operation.
These benefits make oil-immersed transformers a popular choice in many industrial applications, from high-voltage substations to manufacturing plants.
5. Applications of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers are used in various applications, particularly in power generation and distribution systems:- Power Stations: To step up or step down the voltage between the generator and the transmission lines.
- Substations: They help reduce the voltage from high transmission levels to lower levels suitable for distribution to homes and businesses.
- Industrial Facilities: Many factories and large plants rely on these transformers to power heavy machinery.
- Renewable Energy Systems: In solar and wind power facilities, oil-immersed transformers are often used to integrate energy generated at high voltages into the grid.
6. Safety Considerations and Maintenance
While oil-immersed transformers are designed to be safe and reliable, regular maintenance is key to ensuring their longevity. Common maintenance practices include:
- Oil Inspection and Replacement: Transformer oil must be checked periodically for contamination or degradation. Over time, the oil can become acidic or contain moisture, which can compromise its insulating properties.
- Pressure Testing: Monitoring pressure inside the tank is crucial to ensure there are no leaks and that the oil is properly circulating.
- Radiator and Bushing Inspection: These components must be checked for corrosion or mechanical damage.
Proper maintenance reduces the likelihood of power outages and ensures that the transformer operates safely throughout its life.
Oil-immersed transformers are crucial components in electrical power systems, providing safe, reliable, and efficient power distribution. Their ability to cool and insulate the electrical components makes them indispensable in high-voltage and high-load applications. By understanding how oil-immersed transformers work, their benefits, and how to maintain them, engineers can ensure that these essential devices perform optimally, minimizing the risk of failure and supporting efficient power delivery systems.
As the demand for energy continues to grow and renewable energy sources expand, oil-immersed transformers will continue to play an important role in the modernization and sustainability of electrical infrastructures worldwide.









2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)