Complete Guide to Power Pole Transformer Structural Design(2025)
As population and urbanization grow, and users demand greater reliability in power distribution, utility pole transformers remain an essential component of modern infrastructure. This guide explores the structural design of utility pole transformers, covering key concepts, transformer schematics, components, installation strategies, and engineering practices that meet the 2025 standard.
1. What is a Electric Pole Transformer?
A power pole transformer (also called a pole distribution transformer or electric pole transformer) is a distribution transformer mounted on a utility pole. Its core function is to step down medium voltage (e.g., 11kV – 33kV) from the distribution lines to a usable level (e.g., 120/240V) for homes or businesses.
These transformers are commonly seen in rural areas, suburban streets, and industrial complexes. They are cylindrical or rectangular, often oil-filled, and designed for outdoor, long-term operation.
Key Functions:
- Voltage Reduction: Converts medium voltage from primary lines to safe secondary voltages.
- Power Isolation: Electrically separates high-voltage and low-voltage sides.
- Localized Distribution: Supports residential, agricultural, or light commercial loads.
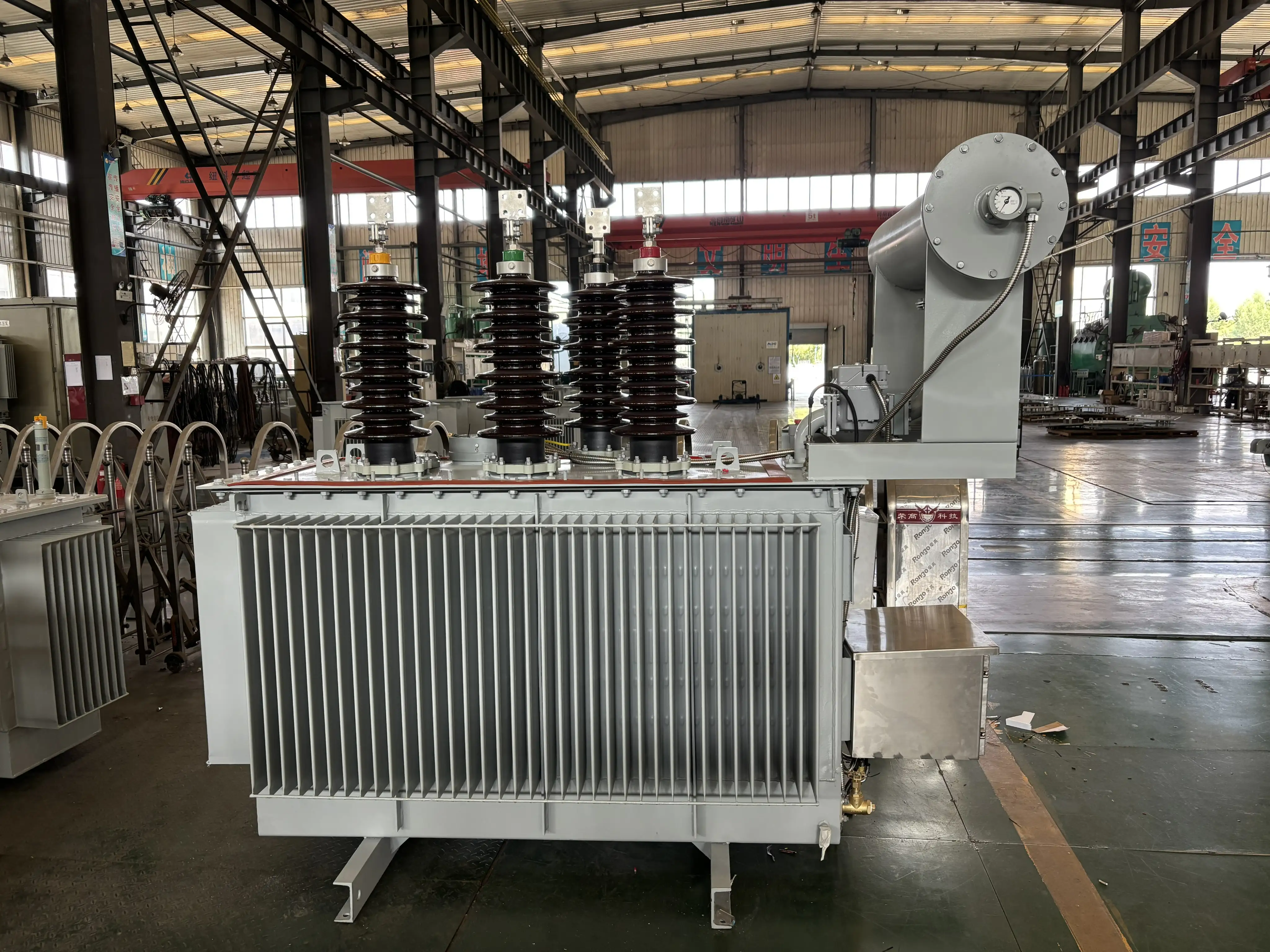
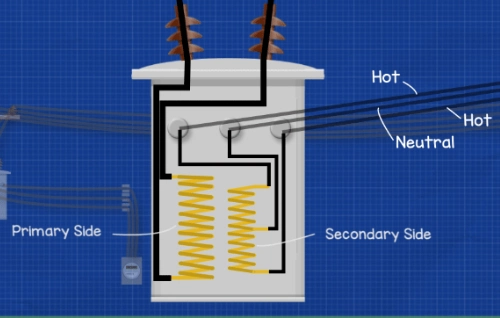
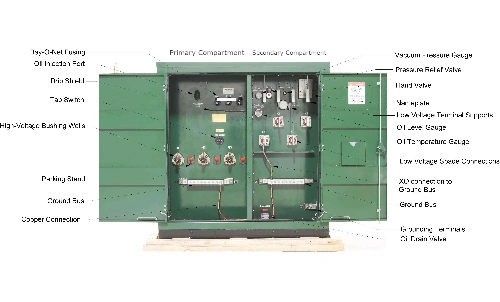
2. Power Pole Transformer Diagram and Main Components
A typical power pole transformer diagram includes:
- High Voltage Input (HV bushings)
- Primary protection (fuse cutouts, lightning arresters)
- Magnetic core and windings
- Tank with insulating oil
- Low Voltage Output (LV bushings)
- Mounting brackets or crossarms
This setup is usually mounted 20–30 feet above ground level on wooden or concrete poles. Fuses and surge arresters protect the transformer from faults, while the oil provides insulation and cooling.
3. Structural Design Considerations for Pole Distribution Transformers
When designing the structural setup of a pole distribution transformer, engineers must account for:
A. Pole Load and Stability
- The weight of the transformer (often 100–300 kg for single-phase units)
- Wind loads on both the pole and transformer
- Ice or snow accumulation in cold regions
B. Clearance Requirements
- Maintain safe clearance from the ground, buildings, and roads
- Comply with national codes like NESC (US) or IEC standards
C. Mounting Hardware
- Steel brackets, crossarms, pole bands
- Corrosion-resistant materials (hot-dip galvanized steel)
- Vibration-resistant anchoring
D. Environmental Protection
- Use sealed, oil-filled tanks for rain/dust resistance
- Include wildlife guards, lightning arresters
4. Types of Pole Mounted Transformers
Pole-mounted transformers come in several types depending on application, phase, and protection level.
A. By Phase Configuration
- Single-phase pole mounted transformer: Common in rural and residential areas.
- Three-phase pole mounted transformer: Used in commercial or industrial zones.
B. By Protection Type
- Conventional: External protection (cutouts, surge arresters)
- CSP (Completely Self-Protected): Internal circuit breakers, fuses, and lightning arresters
C. Specialized Units
- Autotransformers
- Step-up/step-down isolation transformers
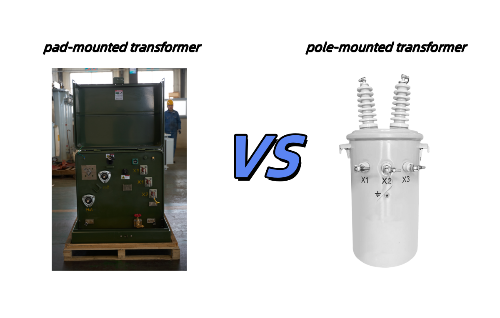
5. Comparison: Pole Mounted vs. Pad Mounted Transformers
|
Feature |
Pole Mounted Transformer |
Pad Mounted Transformer |
|
Installation Location |
Elevated on poles |
Ground-mounted on concrete pads |
|
Space Requirement |
Low (overhead) |
High (requires secure enclosure) |
|
Safety for Public |
Less accessible |
Lockable tamper-proof enclosures |
|
Maintenance Accessibility |
Requires aerial lift or climbing |
Easy ground access |
|
Typical Applications |
Rural, remote, or overhead systems |
Urban, underground cable systems |
Pad mounted transformers are preferred for urban areas with underground systems, while pole-mounted transformers are ideal for overhead distribution in open or rural environments.
6. Transformer Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing a power pole transformer involves:
- Core Construction: Laminated silicon steel cores for low losses
- Winding: Copper or aluminum windings (layer or disk type)
- Assembly: Core and coil placed into steel tank
- Insulating Oil Filling: For dielectric strength and heat dissipation
- Testing: Voltage withstand, insulation resistance, temperature rise
Modern transformer manufacturing emphasizes:
- High-efficiency materials (e.g., amorphous cores)
- Hermetically sealed designs
- Environmentally safe fluids
7. Integration with Power Lines and Network Planning
Pole transformers are directly integrated into overhead power lines, typically via:
- Primary Taps from 11kV, 22kV, or 33kV feeders
- Neutral grounding
- Secondary distribution lines to service drops
Engineers must consider:
- Phase balancing
- Load estimation (peak and average demand)
- Surge protection coordination
- Smart grid compatibility (IoT-ready sensors)
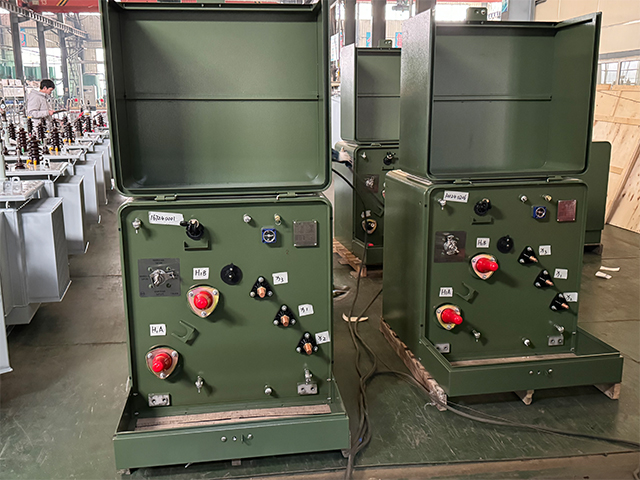
8. Transformer Main Accessories
Key transformer main accessories include:
- Fuses/Cutouts: Overcurrent protection
- Lightning Arresters: Surge protection from lightning or switching
- Bushings (HV/LV): Safe electrical connections
- Pressure Relief Valve: Oil tank pressure safety
- Oil Level & Temperature Gauges
- Mounting Brackets & Insulators
Proper selection and maintenance of these components ensure safe and long-lasting operation.
9. Future Trends and Best Practices (2025 Outlook)
The 2026 outlook for power pole transformers includes:
- Smart Transformers: Real-time monitoring and diagnostics
- Eco-Friendly Fluids: Use of biodegradable ester-based oils
- Compact Designs: Smaller, more efficient units
- Modular Mounting Kits: Faster deployment and maintenance
- Integration with DERs: Solar and EV-ready transformer systems
Engineers should design with adaptability in mind—allowing for future retrofits and remote monitoring capabilities.
In conclusion, Pole-mounted transformers play a critical role in medium-to-low voltage distribution across urban and rural grids. Understanding their structural design—from selection, mounting, component integration, to maintenance—is essential for power engineers and grid planners.
This guide has outlined the technical, structural, and manufacturing aspects of power pole transformers, providing a modern, standards-based perspective for 2025 and beyond. When properly designed and maintained, these transformers ensure safe, efficient, and scalable electrical distribution.









2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)
2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)

H-medium-voltage-power-cable-2.jpg)