Transformer Market 2025 Performance and 2026 Outlook
The global transformer market experienced robust growth in 2025, driven by surging electricity demand, grid modernization, and renewable energy integration. In 2025, the global transformer market was valued at roughly $61.3 billion, with power and distribution transformers accounting for the largest shares. Key end-markets include utility transmission, industrial infrastructure, commercial buildings, and renewables (solar, wind, EV charging). Across all categories, manufacturers are expanding capacity to address a multi-year supply crunch. Notably, Wood Mackenzie reports that U.S. transformer demand has outpaced supply, with power-transformer demand up 119% since 2019 and distribution-transformer demand up 34%. Aging infrastructure (e.g., 40 million US distribution units beyond service life) and new loads (data centers, EV fleets) are key drivers.
Below we summarize 2025 market size (USD and, where available, units/MVA) and segmentation for four transformer types – pad‑mounted, power, dry‑type, and distribution – along with regional highlights (North America, South America, Europe), and 2026 forecasts. Competitive dynamics and leading manufacturers are noted for each category. Where available, key data are tabulated or graphed for clarity.
Pad‑Mounted Transformers
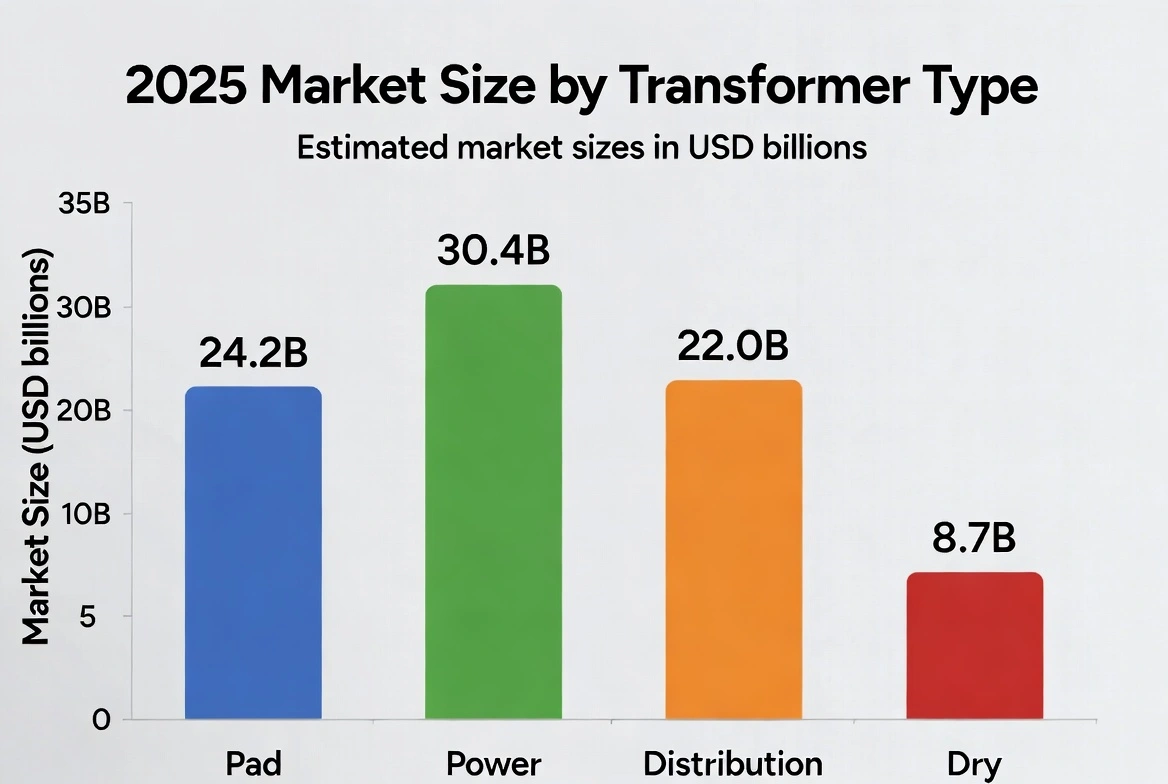
Pad‑mounted transformers (vaulted, ground-level units for distribution voltage) are widely used in residential, commercial, and light-industrial networks. They are built on concrete pads with tamper-resistant enclosures, making them ideal for urban/suburban power distribution, especially near homes, malls, and campuses. In 2025, the global pad‑mounted transformer market was about $24.15 billion. This follows a 2024 base of ~$22.3B (per Global Market Insights) and reflects growth of roughly 8–9%. North America and Europe both see strong pad‑mount demand: the U.S. is expanding distribution grids and adding renewable generation (solar/wind) in residential areas, and European countries (Germany, UK, Spain, Italy, etc.) are investing heavily in smart grids and rooftop solar, boosting pad‑mounted installation. Asia Pacific leads globally – China and India are rapidly urbanizing and electrifying, driving the largest share of new pad-mounted units – but detailed regional breakdowns for 2025 are not publicly reported.
2025 segmentation and drivers: Most pad transformers are three-phase units for multi-family or commercial blocks. In 2025, single-phase pad transformers (<1 MVA) dominated the residential segment. Key growth drivers include rising urbanization, grid expansion, and rooftop solar deployment. Fortune Business Insights notes that “adoption of rooftop solar PV in the residential sector” and massive utility T&D upgrades are boosting pad‑mount demand. However, competition from pole-mount solutions (which require no additional land) is a restraint. The pad‑mount market is also seasonally influenced by infrastructure stimulus; for example, U.S. utility contracts for pad-unit replacements were announced in 2024–25 (e.g,. Mohawk Valley Utility replacing several units).
Forecast (2026): Fort. Business Insights forecasts pad‑mount revenue to grow from $24.15B in 2025 to $25.77B in 2026, a CAGR of ~6.7% (2025–2034). We therefore expect ~6–7% growth in 2026, reaching roughly $26–27 billion globally. Growth will be driven by the same factors (solar build-out, grid refresh) and a chronic shortage of pad transformers in NA (WoodMac projects worsening shortages in 2026 due to data-center and EV charger loads). The new U.S. and Canadian manufacturing expansions (e.g., Hitachi Energy’s major investments) may start to ease lead times, but demand is expected to stay strong.
Competitive landscape: Major pad-mounted transformer manufacturers include ABB (Hitachi Energy), Schneider Electric, Eaton, Prolec GE, Siemens Energy, CG (General Electric), Sunbelt Transformer, Olsun Electric, Wenzhou Rockwell, Ermco, Pearl, and Hitachi America. These firms supply standard pad units as well as modular designs (e.g., factory-integrated switchgear). In 2025–2026, companies are expanding capacity (e.g,. Eaton’s $340M US investment for 3-phase pads) and innovating on smart-pad units (embedded sensors for monitoring). The market remains fragmented regionally, with local players (e.g., Transformers companies in Brazil and Asia) also present.
| Category | Global Market (USD) | Notes |
| Pad‑Mounted (2025) | $24.15B | Dominated by U.S./EU/China demand; three-phase units in utility & commercial networks:contentReference[oaicite:27]{index=27} |
| Power Transformer (2025) | $30.38B | High-voltage units (HVDC, substations); see below |
| Dry‑Type (2024) | $8.1B | Air/solid insulation; see below |
| Distribution (2024) | $21.05B | Overall dist. transformers (includes pad/pole); see below |
Power Transformers
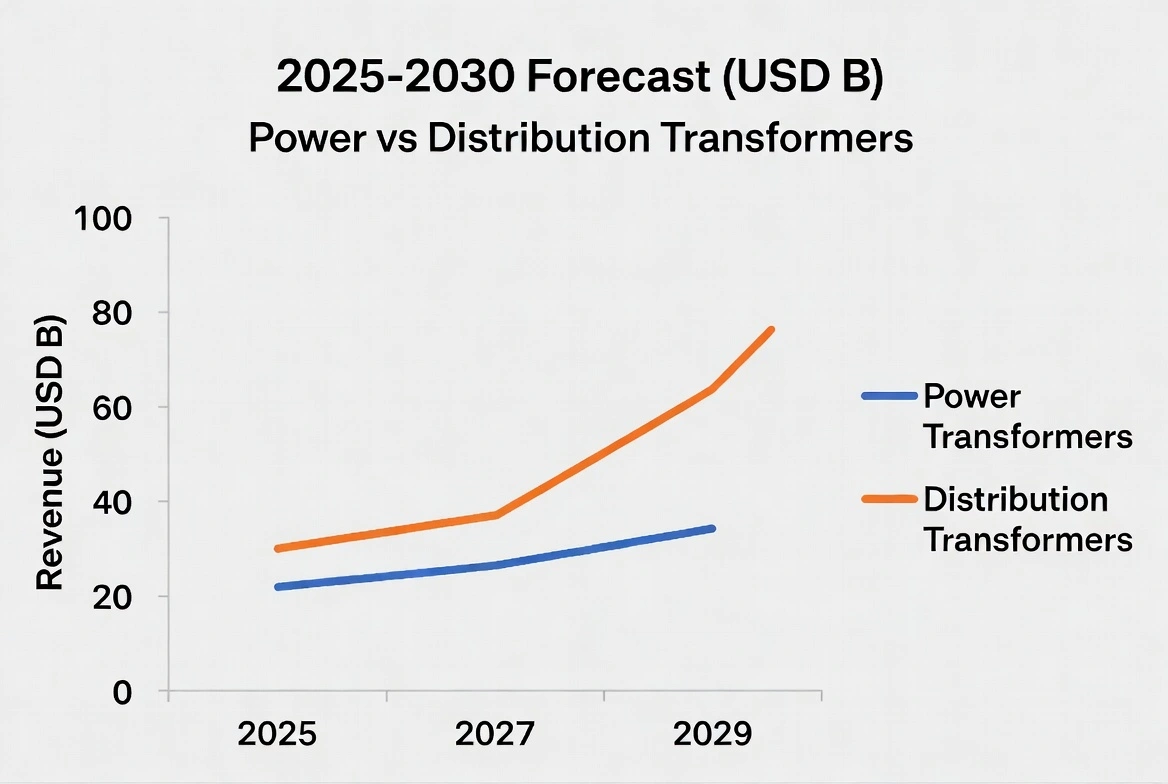
Power transformers step up/down transmission voltages (usually 100–765 kV and above) and are critical for utility grids and large industrial systems. In 2025, the global power transformer market was about $30.38 billion. This includes generator step-up (GSU) and substation transformers. Market growth is driven by global grid reinforcement, renewable power evacuation, and smart‐grid projects. According to MarketsandMarkets, the market is expected to grow at ~6.5% CAGR, reaching $41.62B by 2030. Key factors include rising electricity demand, HVDC adoption, and utility modernization.
Segmentation: By cooling, air-cooled transformers (e.g. cast resin, gas) are the fastest-growing segment, owing to tighter fire/environmental regulations in urban installations. By power rating, medium power units (61–600 MVA) hold the largest share, as these serve sub-transmission networks and industrial grids. The application split is chiefly transmission vs distribution, but exact data are not public. Utilities and bulk power projects form most demand, with growing contributions from renewables (wind/solar farms) requiring high-voltage links.
Regional performance: Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region (CAGR ~7–8%), driven by China and India’s massive power grid expansions. Europe and North America also see strong demand from grid upgrades and interconnectors. For example, the European HVDC projects (e.g., NeuConnect UK-Germany cable) are spurring large transformer orders. In 2024-25, the U.S. announced several factory expansions for large power units (e.g., Hitachi’s Virginia plant, Siemens’ North Carolina plant) to meet domestic needs, indicating continued investment. South America's demand is smaller but growing with new hydro and renewables.
Drivers and outlook: The trend toward renewable energy requires more and higher-capacity transformers. The increasing use of HVDC for long-distance transmission (e.g., offshore wind farms) is a notable driver. Grid resilience programs (smart grids, microgrids) also boost demand for robust power transformers. On the flip side, power transformer markets face long lead times and cost inflation: Wood Mackenzie notes that since 2019, large power transformer lead times often exceed 2 years, and prices have risen by ~77%. For 2026, the M&M forecast implies ~$32–33B globally (continuing ~6–7% annual growth). Factors like new renewable projects in Europe/Asia and U.S. infrastructure spending are expected to sustain ~6–7% growth in 2026.
Competition: The power transformer market is led by a few global engineering firms. Major players include ABB Group (Hitachi Energy), Siemens Energy, GE Vernova, Toshiba, Schneider Electric, Mitsubishi Electric, CG (Hitachi), and WEG. Recent contracts and investments illustrate the competitive landscape: e.g., LS Electric (South Korea) secured a $123M U.S. contract for ultra-high-voltage transformers; CG Power won a 765 kV transformer contract in India; Eaton is investing $340M in U.S. three-phase transformer capacity. Power transformers are high-technology, capital-intensive products, so long-standing incumbents dominate. In North America, for instance, ABB, GE/CG, Siemens, and Eaton are the largest suppliers.
Dry‑Type Transformers
Dry‑type transformers (solid or air insulated, no liquid coolant) are increasingly favored in safety‐critical and space‑constrained settings (indoor substations, data centers, schools, hospitals). They eliminate oil-leak and fire risks, meeting stricter environmental/fire codes. The global dry-type market was $8.1 billion in 2024. Transparency Market Research projects a CAGR ~7.3% from 2025–2035, reaching $17.5B by 2035. (DataIntelo estimates ~$4.9B in 2023 and 5.4% CAGR to 2032, which is conservative.) Three-phase units dominate (59% share in 2024), reflecting most installations in large buildings and industrial facilities. By output, low/medium-voltage dry transformers (<35 kV) are the bulk of the market. Industrial and commercial segments are largest, driven by construction in manufacturing, healthcare, and renewable-power operations.
Regional insights: In 2024, North America held the largest revenue share (~30%), due to early adoption in utilities and infrastructure. Europe and APAC are also key markets: stringent EU fire-safety standards and rising data-center construction boost European demand, while rapid industrialization in China/India fuels APAC growth. Latin America is smaller but growing. We estimate 2025 revenues ~8.7–9.0B (from 2024’s $8.1B). APAC is expected to outpace others in CAGR due to new grid builds; North America will grow modestly by retrofitting aging oil transformers.
Applications: Dry transformers serve utilities, infrastructure, and industrial applications. They are common in transport (railways, metros), renewable energy plants (local collection stations), and commercial/IT (data centers, high-tech campuses). A key trend is sensor-equipped smart dry transformers for real-time monitoring, enabling predictive maintenance. Because of their safety, dry units are often installed in urban substations and underground vaults where oil is undesirable.
Forecast (2026): Assuming ~7.3% growth, 2026 dry-transformer revenue will be roughly $9.3–9.5B. Growth drivers include the replacement of old oil-filled units in cities and the continued electrification of sectors like EV charging (dry transformers are used in some charging stations for indoor safety). Leading manufacturers like ABB, Siemens, Eaton, Schneider, and Hammond are expanding dry-transformer capacity. New cast-resin designs (better insulation materials) are improving performance, supporting growth.
Key players: Top companies include Hitachi Energy (ABB), Quality Power (US), Hammond Power Solutions (Canada), Siemens, Eaton, Schneider Electric, GE/CG, and Hyosung. (In dry-type, many power transformer manufacturers also compete.) Industry sources note that ABB and Siemens have each announced larger dry-transformer factories recently. For example, ABB acquired SEAM (asset management services) in 2024 to enhance transformer lifecycle management, signaling a focus on advanced products.
Distribution Transformers
“Distribution transformers” generally refers to all transformers operating at distribution voltages (up to ~35 kV) and serving end-user networks – including pad-mounted, pole-mounted, and small station units. The global distribution transformer market was about $21.05 billion in 2024. (This figure overlaps partially with the pad-mounted figure above; however, market research often treats pad-mounted as a subcategory.) IMARC projects growth to $31.4B by 2033 (CAGR ~4.3%). MarketsandMarkets (2025 base) estimates $21.40B in 2025, rising to $29.57B by 2030 (CAGR ~6.7%). These surveys reflect steady growth as utilities upgrade networks and support new loads.
Regional breakdown: In 2024, Asia-Pacific led with ~45.6% share (driven by China/India T&D expansion). North America’s distribution transformer market was $12.6B in 2024, projected to grow at ~8.8% CAGR (2025–2034) – notably faster than the global average. Europe’s market was ~$7.1B in 2024, with a 9% CAGR forecast (2025–2034). Latin America and the Middle East/Africa are smaller but growing (e.g., Brazil and Mexico invest in rural electrification). South America’s distribution market (e.g,. Brazil, Argentina) is tied to mining and urbanization, with mid-single-digit growth.
Segmentation and drivers: By application, the largest segment is utility distribution networks, serving residential and commercial customers. GM Insights reports that utilities (public power systems) will see ~7–8% CAGR in the U.S., fueled by grid modernization projects. Industrial and residential/commercial end-markets form smaller slices. Drivers include urban population growth, EV charging infrastructure, and renewable integration (e.g., many EV chargers and rooftop panels require local step-down transformers). For instance, increasing EV penetration in Europe (where BEVs hit ~20% in 2024) is expanding transformer demand for charging stations. Regulatory push for energy-efficient equipment (loss minimization) also drives the replacement of old transformers with new units.
Forecast (2026): Assuming ~4–5% growth, global distribution transformer revenue in 2026 will be on the order of $22–23B. U.S. and Europe will grow faster (~6–9% annually in the near term). For example, the GM Insights Europe report expects $7.1B in 2024 to reach $16.9B by 2034 (9% CAGR), implying ~7% growth in 2025–26. In North America, the $12.6B 2024 market (pad, pole, station units combined) is forecast to exceed $18.7B by 2034, a CAGR of ~8.8%. The continued utility focus on reliability and efficiency – e.g., smart grids and distributed generation – will underpin demand. the
Key players: The competitive landscape is similar to that of pad-mounted. Major manufacturers include ABB (Hitachi), CG/GE, Schneider, Siemens, Eaton (Powell), Toshiba, Mitsubishi Electric, Hyosung, Hyundai Electric, Itochu (Nikko), and regional players (e.g., WEG in Brazil, CG in India). GM Insights lists key North American players as ABB, CG Distribution, Eaton, GE, Hitachi, Hyosung, Imefy, Mitsubishi, Ormazabal, Schneider, Siemens, Toshiba, Voltamp. Distribution transformers are lower-voltage products, so many vendors overlap with pad-mounted (as pad units are essentially distribution transformer designs). In 2025–26, manufacturers are introducing features like amorphous cores (to cut no-load losses) and smart monitoring. Recent industry news highlights include ABB acquiring SEAM Group (asset-management services for transformers), and utilities ordering advanced ‘smart’ distribution transformers from GE and others (not detailed in public sources).
Outlook and Charts
Overall, all four transformer segments are on growth trajectories in 2026, albeit at varying rates. Pad-mounted and distribution units benefit from rapid urbanization and renewables (CAGR ~6–9%), power transformers grow steadily (~6–7%), and dry-type units grow fastest (~7%+). Drivers include unprecedented T&D build-outs, replacement of aging equipment, and new electricity-intensive sectors (EVs, data centers). Constraints remain: long lead times (often >18 months for large units), higher raw material costs (steel, copper), and supply-chain bottlenecks.
While an exact 2026 forecast depends on regional factors, a summary projection is:
- Pad‑Mounted: ~$26–27B (USD) by end-2026 (c. +6–7% vs 2025).
- Power: ~$32–33B by end-2026 (+6–7% vs 2025).
- Dry‑Type: ~$9.3–9.5B by end-2026 (~+7% vs 2024).
- Distribution: ~$22–23B by end-2026 (+4–5% vs 2025).
Each segment’s forecast assumes continuation of current drivers (grid investments, renewables, safety regulations) and does not account for unforeseen supply shocks. Industry sources uniformly stress the ongoing “transformer shortage” in 2025–26; mitigating this through domestic capacity expansion is a key theme.








2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)