Electricity Science and Safety: 300 Questions on Substations (Part 2)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
50. When a system with a neutral point grounded through an arc suppression coil is operating normally, does the arc suppression coil carry voltage?
A: When the system is operating normally, due to the unbalanced capacitance of the three-phase line to the ground, there is a certain voltage between the neutral point of the network and the ground. The magnitude of the voltage is directly related to the imbalance of the capacitance. Under normal circumstances, the voltage generated by the neutral point cannot exceed 1.5% of the rated phase voltage.
51. Why does the battery self-discharge?
A: The main cause of battery self-discharge is impurities on the plates, which form localized small cells. These small cells then form a short circuit between the two electrodes, causing the battery to self-discharge. Additionally, the different densities of the electrolyte at the top and bottom of the battery cause uneven electromotive force on the upper and lower plates, which can also cause battery self-discharge.
52. Why should the battery be charged and discharged regularly?
Answer: Regular charging and discharging is also called verification charging and discharging. It means that for batteries that are operating on a floating charge, the materials on the plates will undergo a large charge and discharge reaction after a certain period of time to check the battery capacity. It can also detect aging batteries and carry out timely maintenance to ensure the normal operation of the battery. Regular charging and discharging are generally done at least once a year.
53. Why should a resistor be connected in series between traffic lights and DC power supply monitoring lights?
A: The purpose of connecting a resistor in series with a traffic light is to prevent the switch from tripping or closing accidentally if a short circuit occurs in the lamp holder. The purpose of connecting a resistor in series with a DC power supply monitoring light is to prevent the filament or lamp holder from shorting out the DC power supply, and to prevent high power supply voltage from burning out the DC power supply monitoring light.
54. How is the load rate of equipment calculated?
Answer: Load rate = (average value of daily load curve / maximum value of daily load curve) * 100%
55. Why must the neutral point of 110KV and above transformers be grounded before power outage and power supply?
A: China's 110kV power grid generally uses a direct neutral grounding system. During operation, to meet the sensitivity requirements of relay protection devices, some transformers operate with their neutral points ungrounded. However, because overvoltages caused by asynchronous circuit breaker operation can compromise the insulation of these transformers, direct grounding of the transformer's neutral point is required when operating unloaded transformers of 110kV and above.
56. What is voltage quick-break protection?
A: When a short circuit occurs, the busbar voltage drops sharply. When the voltage drops to the voltage protection setting value, the low voltage relay operates, trips the circuit breaker, and instantly clears the fault. This is voltage quick-break protection.
57. What is distance protection?
A: Distance protection uses an impedance element to detect short-circuit faults. The impedance of an impedance element is the ratio of the voltage to the current connected to it: U/I = Z. This is the impedance value from the short-circuit point to the protection installation. Because the impedance of a line is proportional to the distance, it's called distance protection or impedance protection.
58. What is a synchronous circuit?
A: Substations are usually equipped with only one or two common synchronization devices, so a synchronization busbar is required. A voltage transformer is used to take the AC voltage from both sides of the circuit breaker. This voltage is then connected to the synchronization busbar via the synchronization handle of each circuit breaker. From there, the voltage is connected to the synchronization device. This secondary circuit and the connection of the synchronization device are called a synchronization circuit.
59. What is high-frequency protection? What are its advantages?
Answer: High-frequency protection includes phase-difference high-frequency protection and power-direction blocking high-frequency protection. Phase-difference high-frequency protection measures and compares the phase of the current on both sides of the protected line, and uses the carrier communication method of the transmission line to transmit the current phase on both sides. Power-direction blocking high-frequency protection compares the direction of power on both sides of the protected line, and stipulates that the power direction from the busbar to a certain line is positive, and the power direction to the busbar is negative. If there is an internal fault in the line, the power direction on both sides is from the busbar to the line, the protection action trips, and the signal transmission method is the same. The biggest advantages: it can cut off various faults from both sides of the protected line without time limit; it does not need to coordinate with the protection of adjacent lines; the phase-difference high-frequency protection is not affected by system oscillations.
60. What are the main physical properties of SF6 gas?
Answer: SF6 gas is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic and non-flammable inert gas with excellent insulation properties. It will not age or deteriorate. Its specific gravity is about 5.1 times that of air. It liquefies at -62 degrees Celsius under standard atmospheric pressure.
61. What are the regulations for installing gas relays on transformers and factory transformers?
Answer: Transformers of 800KVA and above with oil pillows, 400KVA thermal power plant transformers and 180KVA and above hydropower plant transformers should be equipped with gas relays.
62. Why is the temperature rise of Class A insulation transformer windings specified at 65 degrees?
Answer: During operation, the transformer will generate iron loss and copper loss. These two losses are all converted into heat, causing the iron core and winding to heat up, the insulation to age, and affecting the service life of the transformer. Therefore, international regulations require that the insulation of transformer windings should mostly use Class A insulation, and the temperature rise of the winding is stipulated to be 65 degrees.
63. What are the five main components of a resistor-limited on-load tap-changer? What are their uses?
Answer: The components and functions of a resistor current-limiting on-load tap-changer are as follows: ( 1 ) Diverter switch: used to switch the load current; ( 2 ) Selector switch: used to switch the pre-selected tap. ( 3 ) Range switch: used for reversing or coarse tap adjustment. ( 4 ) Operating mechanism: the power part of the tap changer, with functions such as interlocking, limiting, and counting. ( 5 ) Rapid mechanism: rapid switching according to a predetermined program.
64. What is the function of the thermal syphon filter installed on one side of the transformer oil tank?
A: Transformer oil gradually becomes dirty and oxidized during operation. To extend the oil's lifespan and keep the transformer operating under optimal conditions, it's important to maintain good oil quality. A thermosyphon filter can help maintain good quality during transformer operation without significant aging. This allows the oil to last for many years without requiring special regeneration.
65. What is the unbalanced current of a transformer? What are the requirements?
A: Transformer unbalanced current refers to the current difference between the three-phase transformer windings. In a three-phase, four-wire transformer, the load imbalance between each phase must not exceed 20%. In a three-phase, four-wire transformer, the neutral current caused by the unbalanced current must not exceed 25% of the rated current of the low-voltage winding. If these requirements are not met, the load should be adjusted.
66. Why is it necessary to measure the slope of the transformer cover and oil conservator connecting pipe after a new transformer is installed or overhauled? What is the standard?
A: The transformer has two slopes on the gas relay side. One is the slope of the transformer cover, facing the gas relay, which should be 1%-1.5%. This slope should be padded from the bottom during transformer installation. The other is the slope from the transformer tank to the oil pillow connecting pipe, which should be 2%-4% ( this slope is set by the manufacturer ). These two slopes are designed to prevent air from accumulating inside the transformer and to facilitate the rapid and reliable flow of gas into the gas relay in the event of a fault, ensuring proper operation.
67. Which part of the winding is hottest when the transformer is operating normally?
A: The temperatures of the windings and core are higher at the top and lower at the bottom. Experience has shown that for oil-immersed transformer windings of general structure, the hottest point is 70%-75% of the height, and one-third of the way from the inner diameter of the winding. The hottest point for each transformer winding should be determined through testing.
68. What role does the phase regulator play in the power system?
Answer: The function of the phase regulator is to supply reactive power to the system, improve the power factor, reduce the loss in the network, and play a good role in adjusting the network voltage and improving the power quality.
69. What are the basic requirements for main electrical connections?
Answer: ( 1 ) It should have a reliable power supply. ( 2 ) It should be safe and flexible in operation. ( 3 ) It should be simple and easy to operate. ( 4 ) It should be economical in construction and operation. ( 5 ) The possibility of future expansion should be considered.
70. What are the measures to improve the static stability of the power system?
Answer: ( 1 ) Reduce the inductive reactance of each system component. ( 2 ) Use an automatic excitation control device. ( 3 ) Use a frequency-dependent load reduction device. ( 4 ) Increase the active power and reactive power reserve capacity of the power system.
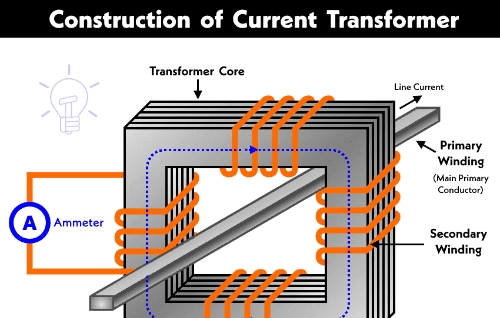
71. What level of current transformer should be equipped for various electricity meters in substations?
Answer: Active energy meters should be equipped with current transformers with an accuracy level of 1.0 or 2.0; reactive energy meters should be equipped with current transformers with an accuracy level of 2.0 or 3.0; energy meters for transformers, station transformers and lines, and other energy meters used to calculate electricity charges should be equipped with current transformers with an accuracy level of 0.5 or 1.0.
72. What is compound rectifier? How many types of compound rectifiers are commonly used?
A: A compound rectifier consists of a voltage-stabilized power supply (voltage source) connected to the voltage system and a rectified power supply (current source) connected to the current system, connected in series and parallel. This ensures a reliable and controlled power supply in all operating modes of the primary system and in the event of a fault. Common compound rectifiers are single-phase and three-phase. Single-phase compound rectifiers can be connected in parallel or in series.
73. What are the dangers of frequency division resonance overvoltage?
Answer: Frequency division resonance is extremely harmful to the system. Under the action of frequency division resonance voltage and power frequency voltage, the magnetic density of the PT core will be saturated quickly, and the excitation current will increase rapidly, which will cause the PT winding to overheat severely and be damaged (all PTs in the same system are threatened), and even cause bus failure and large-scale power outage.
74. What factors are related to the changes in transformer oil level?
A: Under normal circumstances, the transformer's oil level changes with oil temperature. This is because temperature changes directly affect the volume of the transformer oil, causing the oil level in the oil gauge to rise or fall. Factors that affect oil temperature include load changes, ambient temperature changes, internal faults, and the operating status of the cooling device.
75. What are the causes of failure of the on-load tap-changer of the on-load tap-changing transformer?
Answer: ( 1 ) The transition resistor in the auxiliary contact is broken down and burned during the switching process. ( 2 ) The tap changer is not sealed tightly, and water enters, causing a phase-to-phase short circuit. ( 3 ) The contact roller is stuck, causing the tap changer to stop in the transition position, causing a short circuit between turns and burning. ( 4 ) The tap changer tank is low on oil. ( 5 ) A through-fault current is encountered during the voltage regulation process.
76. What is the reason for the failure of the transformer's on-load tap-changing device?
Answer: ( 1 ) The operating power supply voltage disappears or is too low. ( 2 ) The motor winding is broken and burned, and the starting motor loses voltage. ( 3 ) The interlocking contacts are in poor contact. ( 4 ) The rotating mechanism is tripped, and the pin falls off.
77. What should you pay attention to when replacing the desiccant in the transformer breather?
Answer: ( 1 ) The heavy gas protection should be changed to a signal. ( 2 ) When removing the respirator, the connecting pipe should be blocked to prevent back-inhalation of air. ( 3 ) After replacing the dry desiccant, the oil seal should be submerged above the exhalation nozzle to seal the respirator.
78. Can the operating condition of a running transformer be judged based on the sound it produces?
A: You can judge the transformer's operating condition by its sound. Place one end of a wooden stick on the transformer's oil tank and the other end to your ear and listen carefully. If there's a continuous humming sound that's louder than usual, check the voltage and oil temperature. If there are no abnormalities, the core is likely loose. If you hear a squeaking sound, check the bushing for flashover. If you hear a crackling sound, it indicates internal insulation breakdown.
79. What are the basic requirements for relay protection?
Answer: According to the tasks that relay protection devices perform in power systems, relay protection devices must meet the following four basic requirements: selectivity, speed, sensitivity and reliability .
80. Why is it required that relay protection devices act quickly?
Answer: Because the rapid action of the protection device can quickly cut off the fault, prevent the expansion of the accident, and prevent the equipment from being more seriously damaged. It can also reduce the time that fault-free users work under low voltage and the power outage time, and speed up the process of resuming normal operation.
81. What is acceleration after reclosing?
A: When a fault occurs in the protected circuit, the protection device selectively disconnects the faulty circuit and simultaneously activates the reclosing circuit breaker. If the reclosing circuit breaker is a permanent fault, the protection device immediately and indiscriminately opens the circuit breaker again without a time limit. This type of protection is called post-reclosing acceleration and is generally implemented by adding an intermediate relay.
82. What is automatic reclosing?
Answer: When a circuit breaker trips, the device that can automatically reclose the circuit breaker quickly without manual operation is called an automatic reclosing device.
83. What are the characteristics of ground distance protection?
Answer: ( 1 ) It can protect against various ground faults, and only one distance relay is needed, which simplifies the wiring. ( 2 ) It can allow for a large ground transition resistance. ( 3 ) The protection action is fast and has good action characteristics. ( 4 ) It is less affected by changes in the system operation mode.
84. What are the characteristics of battery plate sulfation during operation?
Answer: ( 1 ) Bubbles appear too early during charging or as soon as charging starts. ( 2 ) The voltage is too high during charging and drops below normal during discharge. ( 3 ) The positive plate appears brown with white spots.
85. What causes the transformer to lack oil?
Answer: ( 1 ) The transformer has been leaking oil for a long time or a large amount of oil. ( 2 ) When repairing the transformer, the oil was not replenished in time after draining. ( 3 ) The capacity of the oil pillow is small and cannot meet the operating requirements. ( 4 ) The temperature is too low and the oil storage capacity of the oil pillow is insufficient.
86. What are the characteristics of a battery plate short circuit during operation?
Answer: ( 1 ) The voltage is relatively low (sometimes zero) during charging or discharging. ( 2 ) The specific gravity of the electrolyte cannot increase during charging. ( 3 ) There are a few bubbles during charging, and the bubbles occur later.
87. What are the characteristics of battery plate bending during operation?
Answer: ( 1 ) The plates are bent. ( 2 ) The plates are cracked. ( 3 ) The lead foam on the cathode plate is swollen and forms mossy nodules.
88. What are the contacts " 5-8," " 6-7," and "2-4 " on a typical circuit breaker operating handle? When are they connected in which position of the operating handle? When are they disconnected in which position?
Answer: 5-8 are closing contacts, which are connected in the " closing " position and disconnected in the " after closing " position; 6-7 are tripping contacts, which are connected in the " tripping " position and disconnected in the " after tripping " position; 2-4 are reclosing discharge contacts, which are connected in the " pre-tripping " and " after tripping " positions and disconnected in the " pre-closing " position.
89. What is the function of relay protection?
Answer: Relay protection devices can respond to faults and abnormal working conditions of electrical equipment and automatically, quickly and selectively operate the circuit breaker to cut off the faulty equipment from the system, ensuring that fault-free equipment continues to operate normally, limiting accidents to the minimum scope, improving the reliability of system operation, and maximizing the guarantee of safe power connection to users.
90. What is the overcurrent protection delay characteristic?
Answer: The curve that shows the relationship between the short-circuit current flowing through a protective device and its operating time is called the protective device's time-delay characteristic. Time-delay characteristics are further divided into definite time-delay characteristics and inverse time-delay characteristics. The operating time of a definite time-delay characteristic is fixed and independent of the short-circuit current. The operating time of an inverse time-delay characteristic is related to the short-circuit current: higher short-circuit currents result in shorter operating times, while lower short-circuit currents result in longer operating times. The short-circuit current and operating time exhibit a specific curve relationship.
91. What are the basic principles of the Electricity Law?
Answer: ( 1 ) The principle that the power industry should develop ahead of time according to the needs of national economic and social development. ( 2 ) The state encourages domestic and foreign economic organizations and individuals to invest in the development of power sources and establish power production enterprises in accordance with the law, and implement the principle of "whoever invests, whoever benefits". ( 3 ) The principle that power facilities and electric energy are protected by the state. ( 4 ) The principle that power construction and power production must protect the environment and prevent public hazards in accordance with the law. ( 5 ) The principle that the state encourages and supports the use of renewable energy and clean energy for power generation. ( 6 ) The principle that power enterprises operate independently, bear their own profits and losses, and accept supervision in accordance with the law. ( 7 ) The principle that the state helps and supports the development of the power industry in remote and impoverished areas of ethnic minorities. ( 8 ) The principle that the state encourages the use of advanced scientific and technological technologies and management methods to develop the power industry.
92. What are the basic principles of power grid operation and management?
Answer: ( 1 ) The power grid implements unified dispatching and hierarchical management. ( 2 ) No unit or individual may illegally interfere with the power grid dispatching.
93. What are the main contents of the Electricity Law?
A: The Electricity Law consists of 10 chapters and 70 articles. Its main contents are: The general provisions define the legislative purpose, scope of application, basic principles for developing the electric power industry, and the electric power management system. The specific provisions cover electric power construction, power production and grid management, power supply and use, electricity prices and charges, rural power construction and rural electricity use, protection and supervision and inspection of electric power facilities, and legal responsibilities, comprehensively regulating the construction and development of the electric power industry. The supplementary provisions stipulate the implementation date of the Electricity Law, which was April 1, 1996.
94. What are the main contents of the power production safety management system?
Answer: According to Article 19 of the Electricity Law, power companies must strengthen production safety management and establish and improve a production safety responsibility system, including the following specific systems: ( 1 ) production safety responsibility system; ( 2 ) production duty system; ( 3 ) operation ticket system; ( 4 ) work permit system; ( 5 ) operation supervision system; ( 6 ) work interruption transfer termination system; ( 7 ) production safety education system; ( 8 ) power facility regular inspection and maintenance system.
95. What should be emphasized in anti-accident drills?
Answer: Lessons learned from accidents and abnormal phenomena that occurred in this company and other companies. ( 2 ) Major defects and weak links in the equipment. ( 3 ) Accidents that may occur before and after the commissioning of new equipment, as well as seasonal accidents that affect the safe operation of equipment. ( 4 ) Special operating modes and weak links in operating techniques. ( 5 ) Major and complex operations of equipment systems.
96. What specific training tasks does the team trainer have responsibilities for?
Answer: ( 1 ) Prepare team training plans and, under the leadership of the team leader, conscientiously implement and strive to complete all training tasks assigned by the branch farm, county bureau, etc. ( 2 ) Organize team members to learn the technical specifications of the equipment under their jurisdiction, familiarize themselves with the equipment conditions and regulations, etc. ( 3 ) Carry out team training activities based on the team members and the team characteristics. ( 4 ) Assist the team leader in daily team training work, such as on-site examinations, safety knowledge Q&A, technical explanations, technical Q&A, accident anticipation, etc. ( 5 ) Assist the team leader in arranging job training for new personnel, supervise and inspect the implementation of the master-apprentice contract, and do a good job in the examination and random testing of new personnel. ( 6 ) Timely register and manage all training and summarize them on schedule, and report the implementation status to the training engineer of the branch farm, county bureau.
97. What is the basic content of training for newly hired production personnel?
Answer: ( 1 ) Education on political ideology, fine traditions, factory history, and discipline. ( 2 ) Education on professional ethics in the electrical industry. ( 3 ) Education on abiding by laws and regulations and being civilized and polite. ( 4 ) Education on relevant laws, regulations and safety production knowledge.
98. What are the training steps for new on-duty personnel before they take up their posts?
Answer: Before new on-duty personnel take up independent duty work, they must go through three stages of training: on-site basic system learning, apprenticeship learning, and trial duty learning. A training plan must be formulated for each stage and the training must be carried out according to the plan.
99. What is the purpose of anti-accident drills?
Answer: ( 1 ) Regularly check the operator's ability to handle accidents. ( 2 ) Help production personnel master the correct methods to quickly handle accidents and abnormal phenomena. ( 3 ) Implement anti-accident measures to help production personnel further master on-site procedures and become familiar with the operating characteristics of the equipment.
100. What is a fully insulated transformer? What is a semi-insulated transformer?
Answer: Semi-insulation is the main insulation of the transformer's winding closest to the neutral point. Its insulation level is lower than that of the end winding. On the contrary, the insulation level of the transformer's head and tail windings is the same, which is called full insulation.
Recommended Reading









2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)