HV Bushing vs LV Bushing in Transformers: Key Differences and Applications
Transformers are crucial devices in modern power systems, playing a vital role in changing voltage levels and achieving efficient power transmission and distribution. The core task of a transformer is to convert high-voltage current into low-voltage current suitable for user applications, or vice versa, thereby minimizing energy loss during long-distance power transmission and ensuring a stable power supply.
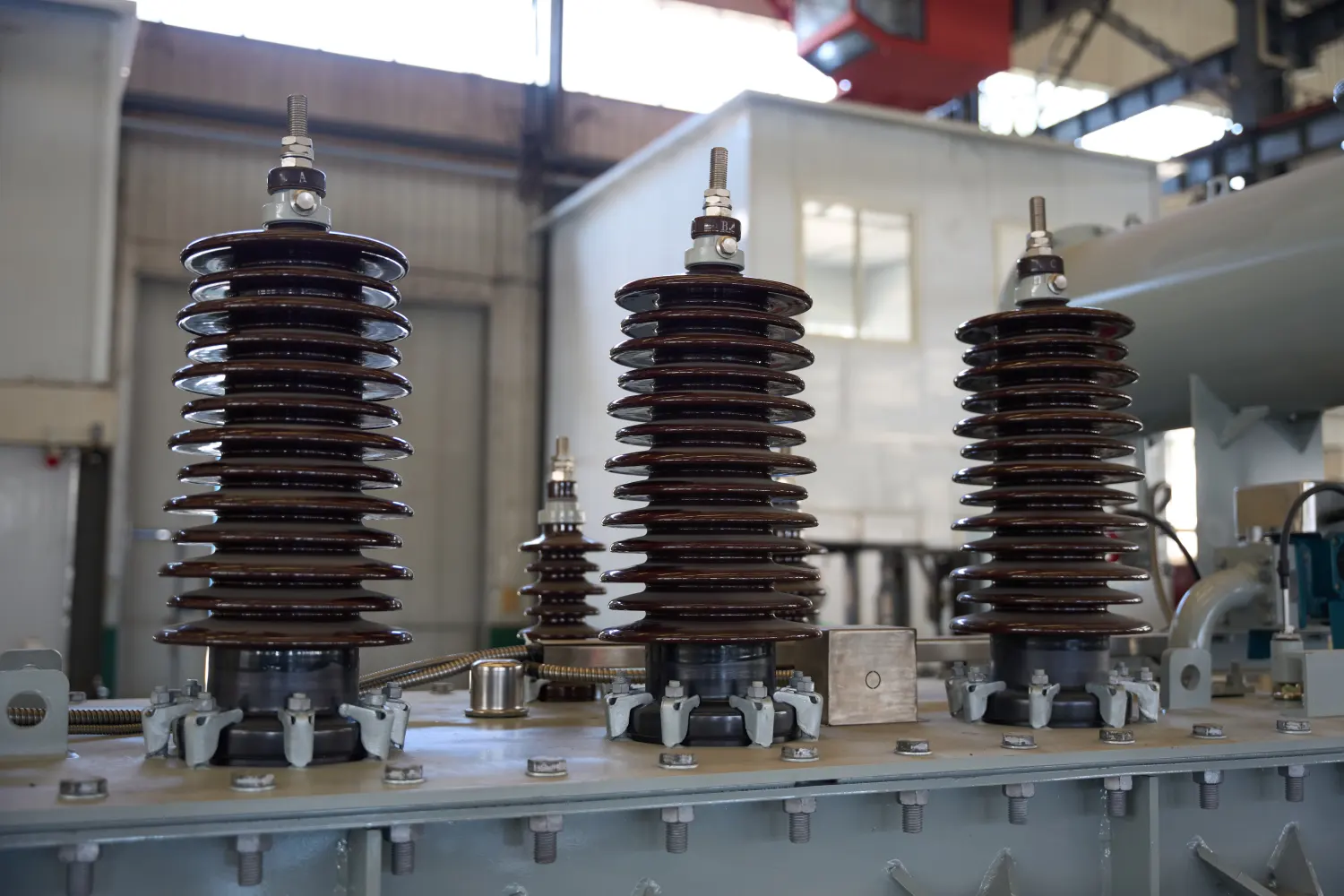
A key component in a transformer is the bushing, which primarily provides insulation protection for the current and allows current to flow safely through the transformer's oil tank. Since the transformer tank is typically sealed, the bushing, through its insulation function, ensures the safe transmission of current, preventing leakage or electrical short circuits. Bushings not only protect the transformer from external environmental influences but also effectively prevent safety hazards such as fires caused by current leakage, ensuring the safe and stable operation of the transformer and the power system.
Transformer bushings are classified into two types according to the voltage they carry: high-voltage (HV) bushings and low-voltage (LV) bushings. High-voltage bushings are mainly used in high-voltage equipment, bearing a greater current load, and therefore have higher requirements in terms of materials and design. High-voltage bushings typically use materials with good electrical insulation, such as ceramics, epoxy resin, or oil-impregnated paper, to withstand higher voltage pressures. Low-voltage bushings, on the other hand, are used in lower-voltage equipment, are usually smaller, and are made of materials such as rubber or polymers, suitable for simpler power distribution systems.
Understanding the main differences between high-voltage and low-voltage bushings helps engineers select the appropriate bushing type, ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and safety of transformer systems in different application environments. Correct bushing selection is crucial for ensuring the normal operation of transformers, avoiding equipment failures and safety hazards caused by incompatible bushing materials or designs.
1. What are HV and LV Bushings?
Bushings are essentially insulated terminals used in transformers to provide a passage for electrical conductors to enter or exit the transformer housing. Their primary purpose is to prevent electrical shorts between the conductors and the transformer tank, while also providing mechanical support.
- HV Bushing: As the name suggests, HV bushings are designed to handle high-voltage applications. These bushings are constructed to manage the high electrical stress that occurs in the transformer, typically from 20 kV to over 1000 kV.
- LV Bushing: LV bushings, on the other hand, are designed for low-voltage applications, generally handling voltages below 1 kV. These bushings allow the low-voltage current to enter and exit the transformer without causing any safety or operational issues.
The HV bushing of the transformer must be designed to withstand much higher voltage stress and is made with specialized materials that can handle the heat and electrical flux of high-power applications.
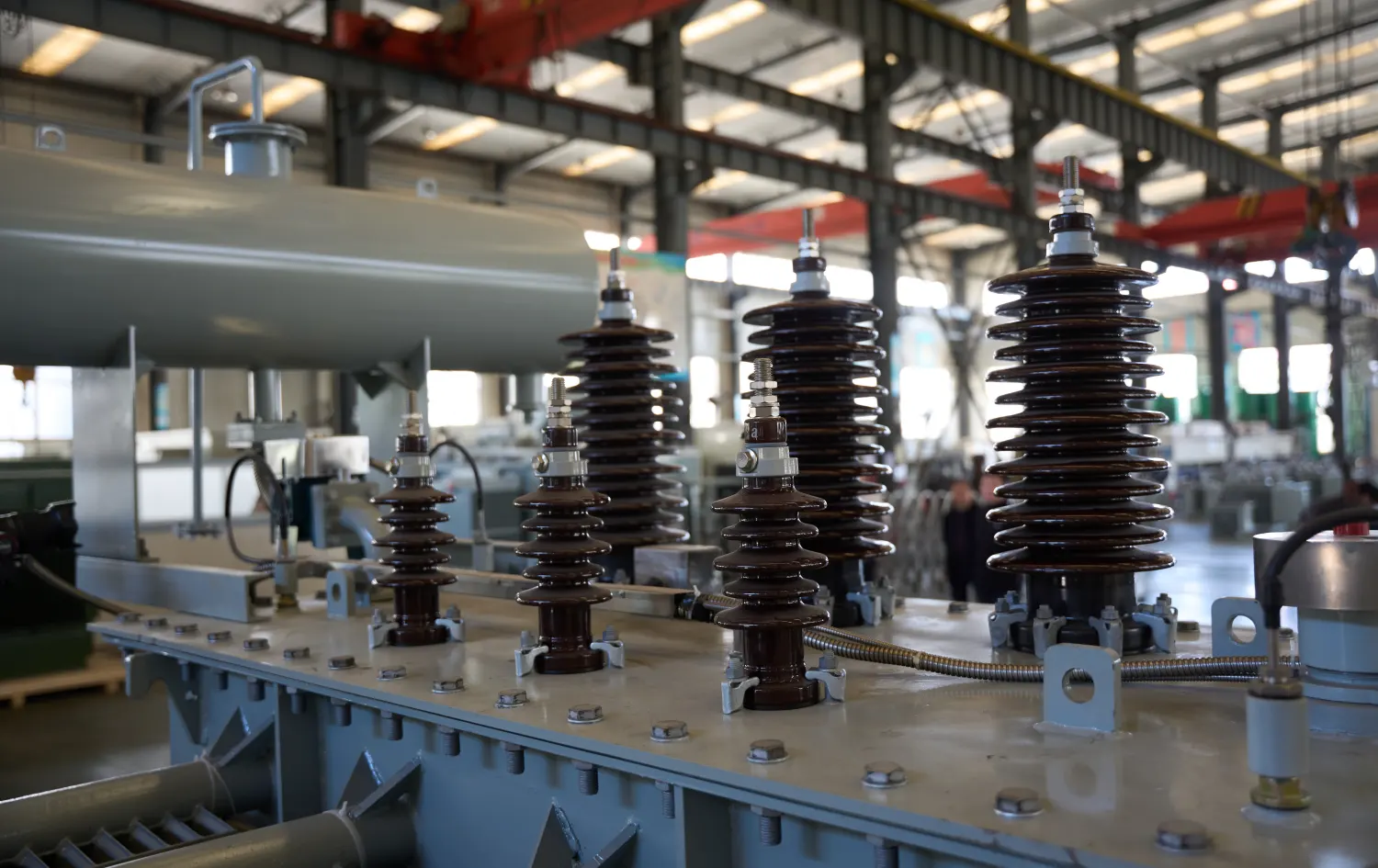
2. Key Differences Between HV and LV Bushings
While both HV and LV bushings perform similar functions, their key differences lie in their design, materials, and the voltage levels they handle. Below is a breakdown of the primary differences:
|
Feature |
HV Bushing |
LV Bushing |
|
Voltage Range |
High voltage (typically 20 kV to 1000+ kV) |
Low voltage (typically below 1 kV) |
|
Insulation Material |
Often uses ceramic, oil, or epoxy |
Typically uses rubber, epoxy, or polymer |
|
Design |
Larger in size, designed for higher electrical stress |
Smaller in size, designed for lower stress levels |
|
Construction |
Often uses oil-impregnated paper for better dielectric strength |
Uses solid insulation or air for lower voltage levels |
|
Function |
Transmits high power across transformer circuits |
Transmits power to lower load devices, like in residential areas |
|
Weight and Size |
Heavier and bulkier, designed to withstand high stresses |
3. Working Principle of HV and LV Bushings
a. HV Bushing Working Principle
HV bushings are designed to provide a safe path for high-voltage current to enter and exit the transformer. The working principle revolves around their ability to insulate the high-voltage conductors from the transformer’s tank, which is grounded. High voltage is passed through the conductor inside the bushing, which is insulated by materials like ceramic, oil, or epoxy. These materials not only prevent electrical shorts but also manage the heat generated by high voltage currents.
The HV bushing of the transformer also has to account for electrical field stress. High voltage levels create significant pressure on the insulation, which is why these bushings are designed with specialized dielectric properties to prevent arcing or electrical failure. The materials used for insulation are chosen for their high breakdown voltage and thermal conductivity.
b. LV Bushing Working Principle
In LV bushings, the working principle is similar, but with lower voltage and electrical stress. Solid insulation like rubber or polymer materials is often used in these bushings. These materials provide adequate insulation for low-voltage currents, ensuring safe transmission of power to homes, businesses, and small industrial facilities. Unlike HV bushings, LV bushings don't require complex insulation systems since they operate at a much lower electrical stress and voltage.
4. Applications of HV and LV Bushings
a. HV Bushing Applications
HV bushings are commonly used in large-scale industrial power transformers and electrical substations, especially those that require high voltage transmission. These transformers are designed to handle large-scale electrical power, and HV bushings ensure that the electrical current is safely transmitted from the transformer to the transmission lines.
Some applications of HV bushings include:
- High-voltage power stations
- Industrial power transformers
- Energy distribution networks
- Utility substations
- Offshore power platforms
b. LV Bushing Applications
On the other hand, LV bushings are typically found in smaller transformers, such as those used for residential or light commercial applications. These transformers step down the voltage to a level that is suitable for home appliances, streetlights, or small businesses.
Some typical applications of LV bushings include:
- Residential transformers
- Commercial transformers for local power distribution
- Street lighting systems
- Small industrial systems
5. Selection and Sourcing of HV and LV Bushings
When selecting HV bushings or LV bushings, it’s essential to consider factors like voltage rating, insulation material, environmental factors, and application requirements. Additionally, sourcing from reliable HV bushing manufacturers ensures high-quality, durable products that comply with industry standards, ensuring long-term operational safety.
Both HV bushings and LV bushings are critical components in transformers, each serving specific functions depending on the voltage level they handle. While HV bushings are designed for high-voltage transmission, LV bushings are used in smaller systems for residential and light commercial applications. Choosing the right bushing for your transformer depends on the voltage requirements, environmental conditions, and safety standards that your system must meet.
Understanding the key differences and applications of these bushings will help engineers, manufacturers, and system designers make informed decisions that optimize the performance and safety of electrical power systems.