Testing standards for Pad Mounted Transformer
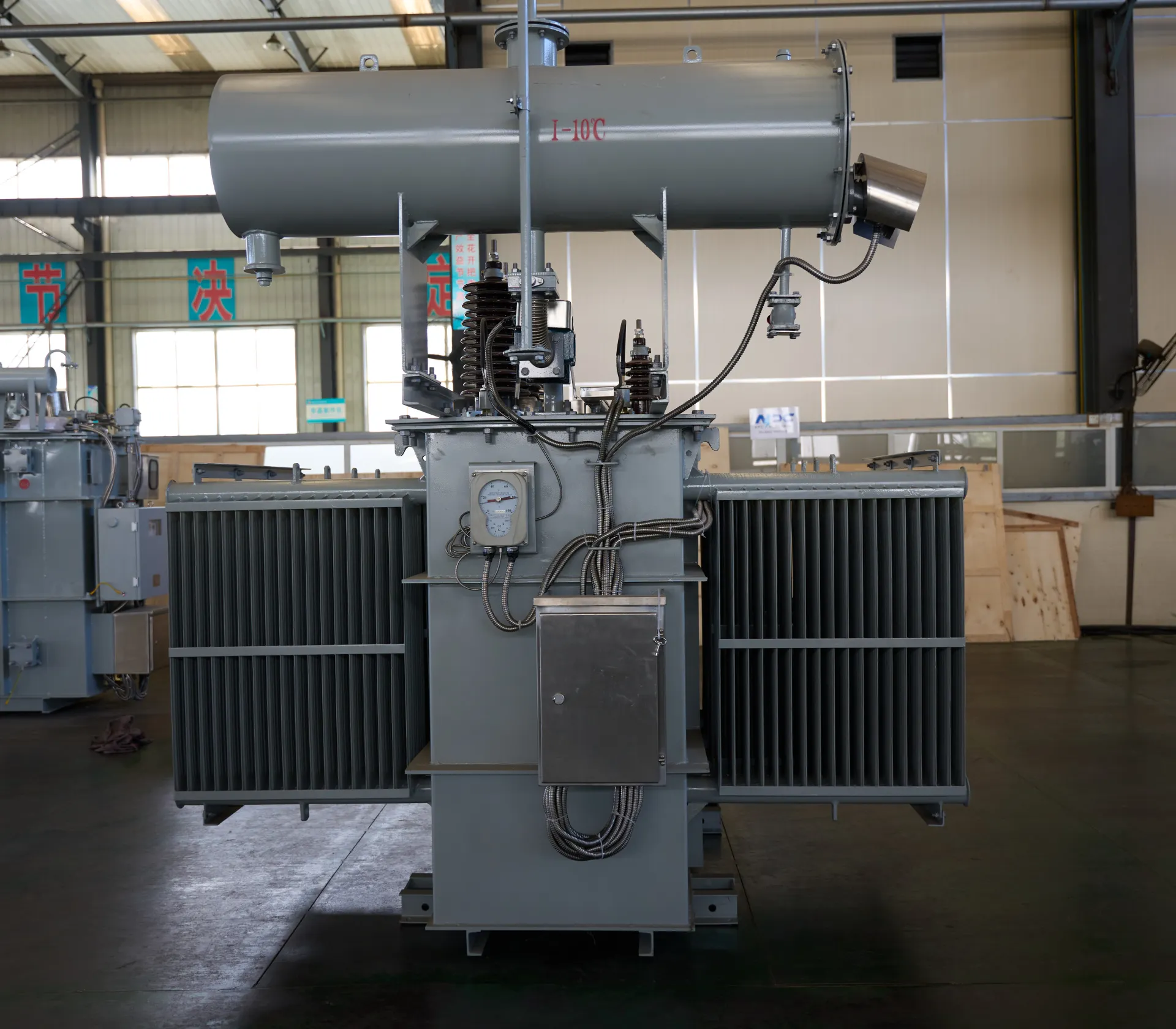
In modern power distribution networks, the pad-mounted transformer is a vital component that ensures safe and efficient voltage conversion. To guarantee long-term performance and public safety, these ground-mounted transformers must undergo a rigorous set of tests before and after installation. In this article, we explore the industry-recognized testing standards for pad-mounted transformers, including those defined by ANSI and IEEE.
Why Testing Matters for Pad-Mounted Transformers
A pad-mounted transformer, whether single-phase or three-phase, operates in outdoor environments where it's exposed to moisture, temperature extremes, and physical disturbances. Regular and standardized testing helps detect manufacturing defects, verify electrical performance, and ensure compliance with international safety and quality benchmarks.
Key Testing Standards and References
1. ANSI C57 Series
The ANSI C57 standards are the primary reference framework for pad-mounted transformer testing in North America. Key documents include:
- ANSI C57.12.00 – General requirements for liquid-immersed distribution transformers
- ANSI C57.12.90 – Standard test code for distribution transformers
- ANSI C57.12.34 – Specific to pad-mounted, compartmental-type, self-cooled transformers
These standards outline the construction, test procedures, and performance expectations for both single-phase and three-phase pad-mounted transformers.
2. IEEE Transformer Testing Procedures
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) provides supplemental guidance and test methodology for electrical transformers. Key testing recommendations include:
- Routine tests: Performed on every transformer unit before shipment
- Design tests: Conducted during product development or upon major design change
- Type tests: Validate performance under normal and extreme conditions
*Compliance with IEEE testing standards ensures pad-mounted transformers meet performance thresholds under real-world conditions.
Types of Tests Performed
Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT)
Before leaving the manufacturing facility, pad-mounted transformers undergo Factory Acceptance Testing, which includes:
- Insulation resistance test
- Turns ratio test (TTR)
- Winding resistance measurement
- Applied voltage and induced voltage tests
- Leakage current and dielectric tests
- Polarity and phase relationship checks
These FAT procedures verify the transformer’s basic electrical integrity and mechanical durability.
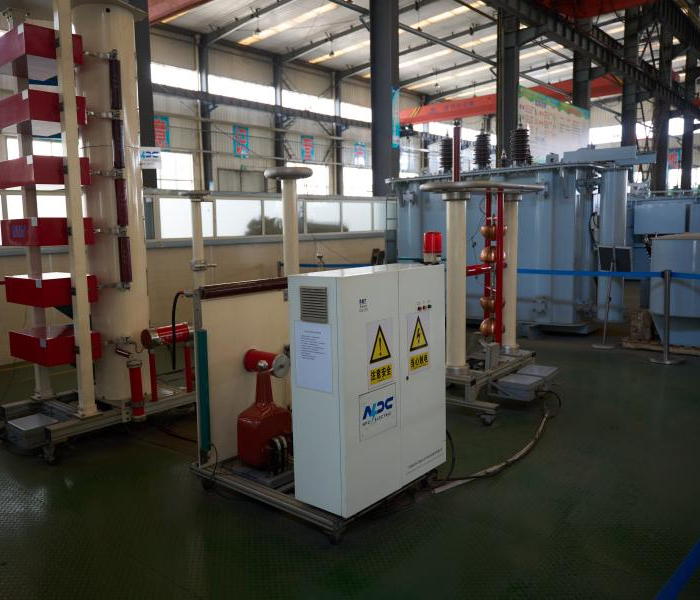
Site Acceptance and Maintenance Testing
After installation, ground-mounted transformer inspections and field tests are critical to ensure proper operation in the real environment:
- Oil quality analysis (for liquid-filled units)
- Infrared thermography
- Partial discharge testing
- Visual inspection for corrosion, gasket failure, and tamper resistance
Routine field tests are recommended annually or biennially, especially for commercial distribution transformers exposed to high load variations.
ANSI/IEEE transformer testing standards and Certification
Manufacturers that follow ANSI/IEEE transformer testing standards typically provide a certified test report along with each unit. This report includes:
- Test methods
- Measured values
- Pass/fail criteria
- Serial number and identification information
This documentation is crucial for procurement teams, engineers, and utility providers, ensuring proper commissioning and regulatory compliance.
Proper testing of pad-mounted transformers is essential to ensure safe and reliable power delivery. By adhering to ANSI C57, IEEE standards, and performing both factory and on-site tests, operators can reduce the risk of failure, extend transformer lifespan, and maintain grid stability. At the same time, we also need to conduct relevant tests on the transformer accessories to ensure safety
Whether dealing with a single-phase residential power transformer or a three-phase commercial distribution transformer, rigorous testing provides the confidence that each unit meets both performance expectations and safety requirements.











2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)